11.02.2025'Roundtable Discussion on Sudan'
Roundtable in Berlin at Ghorfa (Arab-German Chamber of Commerce and Industry) read more11.02.2025'Roundtable Discussion on Sudan'
Roundtable in Berlin at Ghorfa (Arab-German Chamber of Commerce and Industry)
The roundtable discussion on Sudan, hosted by Ghorfa Arab-German Chamber of Commerce and Industry and H.E. Ilham Ibrahim Mohamed Ahmed, Ambassador of the Republic of Sudan to Germany, provided insights into the current geopolitical situation in Sudan. Thank you very much for the kind invitation and for the constructive discussions!
For many years we have been working with partners in Sudan to jointly develop resources in the areas of GeoIT, earth observation and field mapping. Especially, this personal exchange enables us to get deeper insights into local perspectives, which helps us to support our partners and jointly generate and implement good solutions for the respective region or country.
[11.02.2025] 'Roundtable Discussion on Sudan'
Roundtable in Berlin at Ghorfa (Arab-German Chamber of Commerce and Industry) … [read more]

06.11.2024'Hej fra København!'
We are at the EEA in Copenhagen for the ‘CLMS Validation Readiness Meeting’ of our pro... read more06.11.2024'Hej fra København!'
We are at the EEA in Copenhagen for the ‘CLMS Validation Readiness Meeting’ of our project on robust CLMS validation.
Today, we are sending out a 'Hej fra København!' to the European GeoIT community! We are here at the European Environment Agency (EEA) for the ‚Validation Readiness Meeting‘ of our contract about building a cloud-based system for the robust validation of most European CLMS products.
The Copernicus Land Monitoring Service (CLMS) is one of the world's largest databases of publicly available land use and land cover data for the whole of Europe. In an international consortium, we are handling the complexity of validating CLMS products. The project is managed by EFTAS and supported by JBA and COBA.
Here you can find more information on CLMS validation: Link
[06.11.2024] 'Hej fra København!'
We are at the EEA in Copenhagen for the ‘CLMS Validation Readiness Meeting’ of our project on robust CLMS validation. … [read more]

17.09.2024EFTAS at Intergeo Conference
What strategies can local actors use to adapt their activities to the consequences of the climate ... read more17.09.2024EFTAS at Intergeo Conference
What strategies can local actors use to adapt their activities to the consequences of the climate crisis and what role does earth observation data play in this?
The exciting session ‘From Climate Change to Climate Adaptation - Consequences and Measures of Climate Change’ at the INTERGEO Conference will provide answers from the practical side!
The session will be held in German language and will take place as part of our participation in the ‚Copernicus Netzwerkbüro Kommunal‘. It will be hosted by our colleague Dr. Andreas Müterthies. Don't miss it!
- When?
24/09/2024, 15:30 - 16:30 - Where?
Hall C5.1+5.2, INTERGEO Conference
The presentations at a glance:
- 15:30: UrbanGreenEye - Municipal use of climate adaptation indicators based on Copernicus data (Stefan Heiland, City of Leipzig)
- 15:50: From data to decisions - integration of climate data as a key element of climate-resilient urban development (Tim Tewes, City of Constance)
- 16:10: Earth observation data for optimised monitoring of river basin management (Karl-Heinz Spies, Wupperverband)
Are you taking part in the INTERGEO Conference?
Take the chance and visit us at our stand C3.024 in hall 3!
[17.09.2024] EFTAS at Intergeo Conference
What strategies can local actors use to adapt their activities to the consequences of the climate crisis and what role does earth observation data play in this? … [read more]

04.09.2024Intergeo 2024 - How do you make your decisions?
We offer the answer: With Cop4ALL and Digital Twins! read more04.09.2024Intergeo 2024 - How do you make your decisions?
We offer the answer: With Cop4ALL and Digital Twins!
‘What do you use to make your decisions?’ This is the question we are asking people who visit us this year at our Intergeo stand C3.024 in Hall 3. The leading international trade fair for geodesy, geoinformation and land management will take place in Stuttgart from 24 to 26 September. We will be there to answer the ‘with what’ question: With Cop4ALL and Digital Twins!
At a time when sustainable action and environmental aspects take centre stage in all decision-making processes, our innovative solutions support responsible decisions in many application areas:
- Cop4ALL
... provides seamless, ADV-compliant land cover data for the whole of Germany! Our AI-based image analysis combines sentinel satellite images, current orthophotos and in-situ data.
In NRW, cadastral authorities can also calculate customised land cover data and change information.
- Digital twins
... play a decisive role in complex specialised planning processes by simulating the effects of future interventions!
The benefits of such simulations increase with the timeliness of the data. That is why we supply automatically generated, customised data in high temporal and spatial resolution as input for your digital twins.
Visit us at stand C3.024 in hall 3! Find out more about these and many other forward-looking GeoIT services that will sustainably improve your decision-making processes!
We will be happy to reserve a ticket for you. Just get in touch with us! Of course you can also make an appointment with us directly.
- E-mail: intergeo@eftas.com
- Phone: +49 251 133070
We look forward to seeing you in person in Stuttgart!
[04.09.2024] Intergeo 2024 - How do you make your decisions?
We offer the answer: With Cop4ALL and Digital Twins! … [read more]

08.07.2024To Rome for Agricultural Policy!
That was the ICE Conference 2024. read more08.07.2024To Rome for Agricultural Policy!
That was the ICE Conference 2024.
Addressing the current discourse in EU agricultural policy, giving space to new ideas and bringing together experts from all over Europe. That's what the ICE Conference 2024 achieved!
As a city of constant change with its proximity of tradition and modernity, Rome provided an inspiring backdrop for the IACS Community Exchange (ICE) conference at the end of May to discuss the impact of European agricultural policy and the future of the Integrated Administration and Control Systems (IACS) of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP).
For many years, we have been carrying out remote sensing-based inspections of agricultural subsidised areas for numerous federal states, and since the new CAP reform came into force, we have also been carrying out permanent year-round monitoring.
Personal contact with people from the IACS community and the network that has grown over many years are an important base for fast and technically precise communication in these projects.
That is why we were there as a team of four to find out about current developments, challenges and best practices in the field of IACS. The main topics were the implementation of IACS, quality assessments in agricultural systems and new data, methods and tools in agricultural monitoring.
"The intense dialogue showed that we are well equipped for the future requirements of the Common Agricultural Policy with our processes in the field of agricultural monitoring," said Marco Lüth, who coordinates the Agricultural Monitoring business unit at our company, expressing his satisfaction with the conference.
In professional terms: ICE 2024 was a well-rounded event!
And regardless of that: Rome is always worth a visit!
More information about the event can be found on the conference website: Link
[08.07.2024] To Rome for Agricultural Policy!
That was the ICE Conference 2024. … [read more]

17.06.2024Successful mining conference in Abrud
Experts discussed the GoldenRAM project read more17.06.2024Successful mining conference in Abrud
Experts discussed the GoldenRAM project
Mining, sustainability and geodata - these were the topics addressed at the S.C. CUPRU MIN S.A. conference in Abrud, Romania, at the end of May. Our project manager Sebastian Teuwsen was also there to provide information about our role in the new GoldenRAM project.
From May 20 to 22, 2024, experts and interested parties came together to celebrate the 47th anniversary of the founding of CUPRU MIN. The company specializes in the production of copper and copper ore and, with the Roşia Poieni copper mine, owns the largest copper reserve in Romania and the second largest in Europe.
Networking industry and science
One of the focal points of the conference was the GoldenRAM project, which was launched this year and brings together mining stakeholders from all over Europe. A platform is currently being developed to ensure greater transparency in the mining sector and promote cooperation between all stakeholders. “The launch of the GoldenRAM platform represents a significant step forward in geospatial data processing and availability,” said EFTAS project manager Sebastian Teuwsen. He presented how EFTAS is contributing its many years of expertise in the field of remote sensing and mining to the project. “We are the link between the industrial partners and the scientists and help to ensure that the developments are as targeted as possible to specific needs.”
The project coordinators provided exciting insights into the progress of GoldenRAM. Marko Paavola from VTT presented the overall project and the latest developments. Another highlight was the presentation on securing geographical data by Ovidiu Cosma and Dorel Gușat from the Technical University of Cluj-Napoca. They pointed out important principles and practices to effectively protect geodata.
Mapping from above
The project will soon be entering the next round. “The first field campaigns will soon be carried out at the Aitik mine in Sweden and Kevitsa in Finland, as well as in Romania,” explains Sebastian Teuwsen. “In Abrud, various terrestrial samples will be taken and analyzed on site in order to develop new methods in the field of exploration technology, among other things.”
Specifically, the aim is to use XRF detectors to examine the chemical and mineralogical composition of the rocks using X-ray fluorescence analysis. Technical solutions will then be developed to support this mapping from the air using hyperspectral drones in the future.
Further information on the GoldenRAM project, its partners and its objectives can be found at www.goldenram-project.eu.
[17.06.2024] Successful mining conference in Abrud
Experts discussed the GoldenRAM project … [read more]

07.06.2024CLMS General Assembly 2024
It was all about the land in Antwerp! read more07.06.2024CLMS General Assembly 2024
It was all about the land in Antwerp!
Especially about the contribution of Copernicus Land Monitoring Services (CLMS) to policies addressing the planetary crises. That's one of the reasons, why we attended the CLMS General Assembly.
"Easier data access will come with the planned Copernicus Land Data store, a joint activity by JRC and EEA. This underlines the enormous importance of data validation." says our Managing Director Carsten Haub, commenting on one of the outcomes of the event.
On the mentioned subject of data validation we presented our consortium project to set up a cloud-based system for the robust validation of most European CLMS products in the poster session. The project is managed by EFTAS and supported by JBA Consulting Ireland and COBA.
"The inspiring key talk by Janez Potocnik, co-chair of UNEP International Resource Panel, put the importance of resource monitoring into the bigger picture. In doing so, he built a bridge between all aspects of the event." summarises Oliver Buck, our Head of Technology Management, his impressions after the second day.
Thanks to the EEA for the great event!
Want to know more about our contribution to CLMS data validation? You can tune in here: "This is the future of CLMS data validation!"
[07.06.2024] CLMS General Assembly 2024
It was all about the land in Antwerp! … [read more]

04.06.2024Technology transfer as a dialogue:
What does a multicopter in our countryside have to do with coastal protection in Algeria? read more04.06.2024Technology transfer as a dialogue:
What does a multicopter in our countryside have to do with coastal protection in Algeria?
The connection of Algerian coastal protection and multicopters in our countryside is the visit of Mohamed Radhwen Khelifi Touhami, who we hosted in Münster as part of a capacity building training. He is a project manager and geodata expert at the ‘Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit’ (GIZ) in Algeria.
His current project 'PEBLA' aims to protect and sustainably utilise Algeria's unique coastal landscape. By involving the private sector and the tourism industry and by strengthening local stakeholders, the conditions for integrated coastal zone management are improved and new protected areas are created at the same time.
"We regularly exchange ideas with international guests about GeoIT and environmental monitoring in workshops and training sessions." reports Luca Kleinewillinghöfer, who has often worked for us in various African countries. "Based on our current projects, we discussed important aspects of GIS, remote sensing and multicopter mapping with Radhwen, which can be important for modern national park management. With all this, we could forge stable professional links to Algeria and the 'PEBLA' project."
With the best flying weather, we were able to use our multicopters in real life, so that their potential for environmental monitoring could be demonstrated in a very practical way in the countryside.
"The high level of technical expertise combined with the warm and friendly atmosphere really enriched my training at EFTAS." summarises Radhwen after his visit. "Back in 2019, we already worked together to develop a QGIS guide for the management of protected areas in Algeria, which is still widely used and still has the highest number of downloads on our website. This is exactly how international cooperation can advance environmental protection. That's why I'm looking forward to future joint projects and meetings!"
The training of Radhwen also included visits to various national parks and protected areas. Among other things, we discussed there, how to sustainably guide and inform people who visit a protected area in their free time or on holiday.
"We look forward to seeing Radhwen again! In addition to the personal interaction, the exchange with international partners always means an important change of perspective for us." says our colleague Luca, summarising the visit. "We always learn a lot about local conditions. This enables us to consult other stakeholders in the respective regions in a very focused way and develop suitable solutions together with them."
Photos: Mohamed Radhwen Khelifi Touhami with our colleagues Michael Kobs and Martin Schladör during the multicopter training in the Münsterland region.

17.05.2024"We need in-situ data continuity!"
That was our main message at the ESA-Workshop "Earth Observation for Agriculture under Pressu... read more17.05.2024"We need in-situ data continuity!"
That was our main message at the ESA-Workshop "Earth Observation for Agriculture under Pressure 2024"!
During the panel discussion "In-situ: the last hurdle?", Luca Kleinewillinghoefer - our expert for international field campaigns and geostatistics - stressed out the need for continuity in field campaigns.
The earth observation community broadly agrees: EO compatible in-situ data is necessary and important for training, validation, calibration and benchmarking purposes. The amount of EO data arriving almost daily is enormous, and the continuity of the Copernicus services has been ensured. It should be clear, that we do not want to combine these up-to-date mass data sets with inconsistent, outdated in-situ data. Therefore, harmonised European field data campaigns, such as LUCAS or EMBAL, must also to be guaranteed over a long period of time.
In addition, the EO compatibility of EMBAL or LUCAS is on high potential or even already operational. For example, the 'LUCAS Copernicus Module' is specifically designed to lift the information from sample point information up to a Copernicus compatible raster measure. This is supported by the AI-based derivation of land cover from in-situ images taken in all four directions of the sky. But also the expectation of regular reporting and monitoring from agricultural and environmental policies can only be fulfilled, if we see earth observation and in-situ data as a well-balanced pair.
Collecting field data on agricultural land can be challenging, and there is often no clear legal framework for collecting data on private land. During the panel discussion, our colleague Luca highlighted an issue that has already been recognised by the EU: “Gaining farmers’ trust and acceptance on what data we collect and what we do in the fields is important and crucial. It requires careful and clear communication about what information can be disclosed to the public.”
Luca also emphasised the importance of better integrating in-situ data collection into project planning at the tender stage, with timing being particularly crucial. This is our experience from many years of managing the complex task of in-situ campaigns on a European scale.
The panel was chaired by Raphaël d'Andrimont (JRC) and Gilliams Sven (GEOGLAM). José Miguel Rubio Iglesias (EEA), Inbal Becker-Reshef (NASA HARVEST, Univ. Strasbourg), Grégoire Tombez (Green Triangle), Sophie Bontemps (UCLouvain), Steffen Fritz (IIASA) joined our colleague Luca on the panel.
Thank you very much for the invitation! We were happy to share our experiences with field mapping projects on a European scale with the community through this panel!
#FieldDataContinuity #EMBAL #LUCAS #IACS #EO4AGRI
EO4AGRI (13-16 May 2024, Frascati, Italy) was organized by European Space Agency - ESA, the European Commission, FAO, World Food Programme, and GEOGLAM (Group on Earth Observations Global Agricultural Monitoring).
[17.05.2024] "We need in-situ data continuity!"
That was our main message at the ESA-Workshop "Earth Observation for Agriculture under Pressure 2024"! … [read more]

08.04.2024GoldenRAM: A State-of-the-Art Earth Observation Platform for Raw Materials
Horizon Europe project aims to transform raw material information exchange with the GoldenRAM Eart... read more08.04.2024GoldenRAM: A State-of-the-Art Earth Observation Platform for Raw Materials
Horizon Europe project aims to transform raw material information exchange with the GoldenRAM Earth Observation platform, leveraging the latest in IT, Cloud, and AI technologies.
The Technical Research Centre of Finland and 11 partners kicked-off the Horizon Europe project GoldenRAM (GA: 101138153), funded by the European Commission. This 3-year long project aims to enhance raw materials information exchange by developing an Earth Observation Platform which depmarloys the latest advances in IT, Cloud and AI technologies. The platform is designed to facilitate the exchange of accurate information on Raw Materials in Europe and partner countries to support mining companies, stakeholders in the mining industry, and the public.
Europe requires critical raw materials (CRMs) for several key reasons, chiefly among them the continent’s commitment to a sustainable and digital future. CRMs such as lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements are vital for renewable energy technologies, electric vehicles, and digital devices, all of which are central to reduce carbon emissions, achieve climate neutrality and reach the European Union’s Green Deal and digital transition goals. CRMs are however highly vulnerable to supply disruptions, and as global demand for rare earth metals and lithium is set to increase almost six-fold by 2030 according to global technology intelligence firm ABI Research, Europe must ensure strong, resilient, and sustainable value chains for critical raw materials to realise its decarbonisation and digital transition goals.
Project brings experts together
The GoldenRAM platform aims to address some of the key challenges faced by the European mining industry, including environmental sustainability, resource management, and operational efficiency. By providing an integrated and user-friendly platform, the project seeks to foster greater transparency and collaboration between stakeholders, contributing to Europe's CRM goals. By way of several field trials across Europe, the project will demonstrate the potential value of the platform in various stages of the raw materials value chain, from exploration to site closure.
Dr. Marko Paavola, Project Coordinator and Senior Researcher at VTT stated, "GoldenRAM brings together an expert team of mining end users, technology providers, and research organizations. With this platform, we're putting advanced technology to practical use. It's about turning data into decisions that support both industry needs and environmental stewardship, solving today's challenges of the mining industry in a sustainable way".
The consortium behind this project includes some of Europe’s leading tech companies and research institutes, renowned for their expertise in artificial intelligence, earth sciences, and sustainable development in the field of raw materials. Coordinated by VTT (Finland) and Technical Manager OPT/NET (The Netherlands), the consortium partners include BGR (Germany), EFTAS (Germany), GTK (Finland), Technical University of Cluj-Napoca (Romania), GIUA (Ukraine), CloudFerro (Poland), Evenflow (Belgium), and mining companies such as Boliden (Sweden), Cupru Min (Romania), Sokli (Finland), and Savannah Resources (Portugal).
EFTAS contributes remote sensing expertise
EFTAS is contributing its many years of expertise and extensive network in the field of remote sensing to the project. "In the GoldenRAM project, we are working intensively with the industry partners to establish the user requirements," reports EFTAS project manager Sebastian Teuwsen. "These include international mining companies and their sites from Portugal, Sweden, Finland, Romania and Ukraine." The EFTAS team is also responsible for checks and test procedures for the new platform.
For more information about the GoldenRAM project, its partners, and its objectives, please visit www.goldenram-project.eu.
[08.04.2024] GoldenRAM: A State-of-the-Art Earth Observation Platform for Raw Materials
Horizon Europe project aims to transform raw material information exchange with the GoldenRAM Earth Observation platform, leveraging the latest in IT, Cloud, and AI technologies. … [read more]

21.03.2024Copernicus has an impact.
That was the Copernicus Forum 2024 in Berlin! read more21.03.2024Copernicus has an impact.
That was the Copernicus Forum 2024 in Berlin!
The Copernicus program is now the world's largest provider of earth observation data for civil satellite-based earth observation. Copernicus data provides land monitoring with a massive wealth and variety of information, which is processed using stable processes and utilised on a large scale.
Under the headline "Copernicus wirkt." ("Copernicus has an impact."), the "National Forum for Remote Sensing and Copernicus 2024" (19 to 21 March 2024, Berlin) presented examples of best practice, discussed current challenges and formulated expectations for the future design of the Copernicus programme.
We took part in the forum with presentations in the sessions "Municipal Copernicus Applications", "Remote Sensing for Forests in a Changing Climate" and "Land Monitoring - Today and Tomorrow" as well as in the company exhibition:
Cop4ALL-DE - Working together for standardised land cover:
In the session "Land monitoring - today and tomorrow", Thorsten Dahms from the BKG and our EFTAS colleague Sönke Müller jointly reported on Cop4ALL-DE. With the help of Copernicus data, Cop4ALL-DE will in future derive a standardised land cover for the whole of Germany. In addition to an initial look at the service, the scaling of the underlying deep learning approach also played an important role in the two presentations. The initial results from the adaptation of a method developed and already operational in NRW to the whole area of Germany are promising. The aim is to process the first nationwide data by the end of 2024.
How can remote sensing and Copernicus data make it easier for cities, districts and municipalities to fulfil their municipal tasks?
This was discussed in the session "Municipal Copernicus applications: Networking, demonstrating, stabilising." using examples of best practice. The session was hosted by our colleague Andreas Müterthies and Christian Steffens from Copernicus Netzwerkbüro Kommunal.
Forest planning 4.0: New methods and data products for forest inventories
In the session "Remote sensing for forests in a changing climate", our colleague Oliver Buck reported on the modernisation of forest planning using innovative remote sensing methods. He gave a first insight into the "Waldplanung 4.0 - Forstliche Fernerkundung“ (Forest Planning 4.0 - Forest Remote Sensing) project of “Bayerische Staatsforsten” (Bavarian State Forests), which aims to automatically derive specialized forestry products.
So what about the impact and benefits of Copernicus?
In the panel discussion on the first day, the wish was expressed that we should move much further from "Copernicus has an impact." to "Copernicus is used.". The experience of the forum shows: We are in the centre of the utilisation:
"Copernicus is working, as the past three days have proven. More and more services are operational and are establishing themselves as an integral part of the respective specialised data infrastructures," says our Head of Business Development Andreas Müterthies, expressing his satisfaction with the Copernicus Forum 2024. "The fact that we as EFTAS are contributing to the continuity of Copernicus use through Cop4ALL-DE or Forest Planning 4.0 naturally makes us particularly happy!"
The time in Berlin was filled with interesting workshops, intensive discussions and professional input. Many thanks to everyone who made the forum possible, both in front of and behind the scenes. We would love to return!
[21.03.2024] Copernicus has an impact.
That was the Copernicus Forum 2024 in Berlin! … [read more]

11.03.2024Copernicus Land Monitoring Service (CLMS)
This is the future of CLMS data validation! read more11.03.2024Copernicus Land Monitoring Service (CLMS)
This is the future of CLMS data validation!
Imagine the complexity of one of the world's largest databases of publicly available land use and land cover data for the whole of Europe: 170 different datasets with 26 data products - that's the Copernicus Land Monitoring Service (CLMS)!
We are happy to lead an international consortium under a new validation contract that will build a cloud-based system for the robust validation of most European CLMS products over the next four years!
To ensure that the CLMS is highly accurate and meets technical specifications and user requirements, it will undergo a rigorous quality control process. Both new and proven reference data (e.g. from the Copernicus in-situ component) are taken into account in the independent validation. Only in this way, the CLMS can remain the indispensable tool for research, planning and decision-making in a wide range of application areas.
The new validation contract focuses on standardising processes to a greater extent, making them more efficient and carrying out validation very quickly, which means that the data records shall be validated within three months of being created. Part of the concept is also that not only the precision of the products is assessed. Their technical suitability for the intended areas of application will also be evaluated.
At the beginning of March, the project entered its first phase with the kick-off at the European Environment Agency (EEA) in Copenhagen. In this phase, the IT system will be set up, suitable reference data will be prepared and the methods will be defined. This will establish a common CLMS validation framework aimed at consistency and efficiency, as well as transparency, reusability, reproducibility, sustainability and compliance with relevant standards.
As far as operational capability is achieved at the end of the start-up phase, the first validations can be carried out as early as 2024. The CLC+ backbone grid 2018/2021 and the upcoming high resolution layers are planned for this purpose.
The project is managed by EFTAS Fernerkundung Technologietransfer GmbH and supported by JBA Consulting Ireland and COBA.
Further information on Copernicus Land Monitoring Service can be found here:
https://land.copernicus.eu/en
[11.03.2024] Copernicus Land Monitoring Service (CLMS)
This is the future of CLMS data validation! … [read more]

06.02.2024Sustainable management in Münster.
Ökoprofit award - EFTAS recertified once again. read more06.02.2024Sustainable management in Münster.
Ökoprofit award - EFTAS recertified once again.
Sustainably improving the environmental and climate footprint, reducing operating costs and promoting employee motivation - EFTAS was awarded the ÖKOPROFIT® Münster environmental certificate for the first time exactly ten years ago. We have now been recertified for our efforts and were honoured in January together with other Münster-based companies.
ÖKOPROFIT is a co-operation project between more than 100 local authorities, local businesses and other regional and national partners. The concept was originally developed in Graz, and today over 4,000 companies in their respective municipalities are involved in this forward-looking project.
EFTAS has its own environmental team
Sabine Lüth and Benedikt Peter are responsible for environmental and sustainability management at EFTAS - we have them to thank for the successful recertification! Both have been working at EFTAS for many years and have implemented numerous measures together.
Last year, the focus was on increasing energy efficiency in many hardware areas. "Among other things, we invested in a new cooling system for server cooling," Benedikt Peter gives an example. "This saves us around 6,700 kWh of electricity per year and reduces our electricity requirements for server cooling by around 50 per cent." That is roughly the electricity consumption of a five-person household with electrical water warming.
The use of 100% recycled paper saves a further 3.7 kWh of energy and 0.15 tons of CO₂. The new inkjet printer also ensures a better energy balance. "We are currently drawing up a detailed CO₂ balance sheet that we can also use in customer communication," emphasises Sabine Lüth. "We are also further developing the topic of sustainability in our quality management and anchoring it even more firmly in our company policy."
Employees get involved
The EFTAS environmental team is very keen to involve all colleagues. For example, there are regular surveys on environmental issues, from which new ideas are developed. "We have already initiated many measures to promote environmentally friendly mobility," says Sabine Lüth.
EFTAS offers its employees job bike leasing and has purchased an electric company car and a cargo bike. "Flexible arrangements for mobile working also reduce emissions and improve employee satisfaction."
With our endeavours, we are currently one of 138 companies and facilities in Münster that have been Ökoprofit-certified since 2001. The overall outcome is impressive: The companies collectively save more than 30.4 million kilowatt hours of energy, almost 20,108 tons of carbon dioxide, 172,156 million litres of fresh water and 2,064 tons of residual waste per year.
---
Photo (from left to right): Arno Minas (Head of Administration of the Department for Housing Supply, Real Estate and Sustainability of the City of Münster), Olaf Büscher (EFTAS Managing Director), Sabine Lüth and Benedikt Peter (EFTAS environmental team) and Viktor Haase (State Secretary in the Ministry of the Environment, Nature Conservation and Transport of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia) at the awards ceremony. (© Michael C. Möller)
[06.02.2024] Sustainable management in Münster.
Ökoprofit award - EFTAS recertified once again. … [read more]
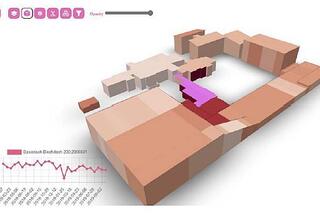
05.07.2023BIMSAR - Efficient Building and Infrastructure Monitoring
AI-based analysis of BIM and SAR data read more05.07.2023BIMSAR - Efficient Building and Infrastructure Monitoring
AI-based analysis of BIM and SAR data
Whether design, construction, renovation or demolition - the Building Information Modelling (BIM) method can be used for the entire life cycle of a construction project. An important role is played by the monitoring of existing buildings and infrastructures, such as railway lines, roads or bridges.
Many objects are affected by ground movements, for example due to post-mining in the Ruhr area. Within the BIMSAR project, a novel approach for the detailed monitoring of building movements was therefore developed. In this way, an important contribution can be made to the longevity of infrastructure objects and sudden failures can be prevented.
AI-based fusion of BIM and SAR
In the BIMSAR project, EFTAS as coordinator and the technical partners are using new methods to merge BIM and radar satellite technology for building monitoring. The basis is an AI-based fusion of SAR data and in-situ data of buildings and transport infrastructures.
The focus is on the innovative combination of new AI methods and model-based data analysis methods to create a hybrid model. The basis is formed by Building Information Modelling data and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data from the Copernicus programme and other radar missions.
4D motion analysis
For building monitoring, multi-temporal radar interferometry methods are used to determine pseudo points on the building. Due to building damage, thermal fluctuations or ground subsidence, each of these points has its own multi-dimensional, spatial and temporal series of movements. With the help of the data, risk levels can be derived for each part of the building in terms of possible movements and damage.
BIM data is used as an in-situ reference for the AI procedures in order to localise so-called persistent scatterers (PS) more precisely for the radar interferometric analysis, to link them with each other and thus to be able to analyse the infrastructure object more precisely in its 4D movement behaviour.
Efficient monitoring
Compared to the classical measurement of ground movements on site, the BIMSAR technique can be applied much more cost-effectively in terms of time and space. For example, data from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 satellites can be used to estimate ground motion every three days for an image scene of 250 kilometres × 180 kilometres under optimal conditions.
For the first time, BIMSAR will enable the use of AI and Copernicus to contribute to highly efficient and accurate satellite remote sensing-based monitoring of infrastructure movements, such as those that can be expected in tunnel construction projects, in mining regions such as the Ruhr region, or even through natural processes such as subrosion.
The BIMSAR project
EFTAS is the project coordinator for BIMSAR. Other partners are the Post-Mining Research Centre of the Georg Agricola University of Applied Sciences (Forschungszentrum Nachbergbau der Technischen Hochschule Georg Agricola, THGA), the Institute for Photogrammetry of the University of Stuttgart, the Office for Geoinformation, Surveying and Cadastre of the City of Essen (Amt für Geoinformation, Vermessung und Kataster, Stadt Essen) and Vivawest Dienstleistungen GmbH. The German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, DLR) is responsible for funding administration.
The BIMSAR project is funded by the Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Action (Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz).
Further information is available here: https://bimsar.eftas.services/
[05.07.2023] BIMSAR - Efficient Building and Infrastructure Monitoring
AI-based analysis of BIM and SAR data … [read more]

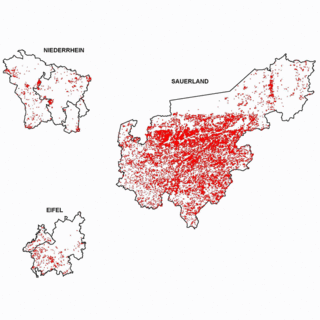
21.02.2023Exploration with remote sensing and AI.
Europe-wide MultiMiner project launched as part of the EU Green Deal. read more21.02.2023Exploration with remote sensing and AI.
Europe-wide MultiMiner project launched as part of the EU Green Deal.
Europe's future depends on a healthy planet. EU member states have therefore set themselves the goal of achieving climate neutrality by 2050. To make the transition to a fair society with a modern and competitive economy, a package of measures with initiatives from different policy areas was agreed in the Green Deal.
One of Europe's growing problems is its dependence on raw materials. In recent years, it has become clear that the commodity market is influenced by factors such as war, sanctions or production restrictions. It is therefore crucial that the EU explores its own potential for raw material production and becomes more self-sufficient. However, domestic extraction of critical raw materials can have environmental impacts that need to be taken into account.
Copernicus data support exploration
The MultiMiner project, launched in 2023 as part of the Green Deal, is dedicated to this challenge. The goal: to create new tools that enable the discovery of additional primary resources in Europe and thus self-sufficiency in raw materials.
A Europe-wide consortium of 12 partners, including EFTAS from Münster, is developing innovative, AI-based solutions by summer 2026, that require little or no data collected on site. Important foundations are formed by satellite data from the European Copernicus programme as well as earth observation data from commercial providers. In addition, data is collected by drones and in-situ surveys.
The developed algorithms will initially be demonstrated at four test sites in Finland, Austria and Greece. In the future, the solutions are expected to improve the safety, environmental impact and cost efficiency of mineral exploration and optimise the monitoring of mine sites.
In addition, MultiMiner aims to increase the transparency of mining by identifying potential environmental impacts as early as possible and storing digital information of currently unminable raw materials for future generations.
Close network between research and application
As a project partner, EFTAS contributes its many years of expertise in the field of remote sensing-based exploration techniques. The company supports a wide range of mining processes with geo-information and geoIT systems, from the development of new deposits to the dismantling of mining sites. In the MultiMiner project, EFTAS forms the interface between research and application.
Further information on MultiMiner is available here:
https://www.esf.org/eu-projects/multiminer/
More about EFTAS services in the field of energy and mining: https://www.eftas.de/anwendungswelten.php#section:energiebergbau
[21.02.2023] Exploration with remote sensing and AI.
Europe-wide MultiMiner project launched as part of the EU Green Deal. … [read more]
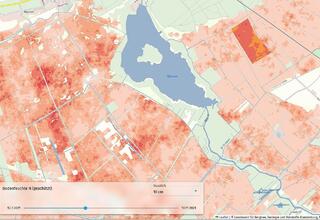
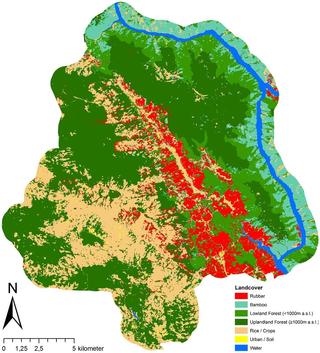
12.04.2023Climate protection through peatland conservation
BEWAMO project completed: Assessment and monitoring of peatlands read more12.04.2023Climate protection through peatland conservation
BEWAMO project completed: Assessment and monitoring of peatlands
Peatlands make up only about three percent of the global land area, but store twice as much carbon as all the world's forests combined. Thus, peatland soils play an important role in climate protection. However, intensive agricultural use and peat cutting in Germany increasingly lead to drainage and thus to the release of large amounts of climate-damaging CO2. Global climate change therefore poses major challenges to the current use of peatlands.
Monitoring soil moisture
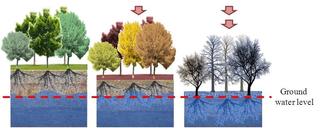
In the BEWAMO project, an evaluation procedure for agriculturally used peatland soils was developed and implemented, taking greenhouse gas avoidance costs into account. Besides the peat thickness, the drainage depth is a main influencing factor for the carbon release potential and stocks.
The control of corresponding rewetting measures is carried out with the help of a monitoring procedure in which the moisture status of the peatland soils is observed over a wide area using satellite remote sensing. EFTAS has developed remote sensing-based processes for this purpose in order to present reliable information on the soil moisture and land cover of peatland areas in time and space on the basis of the sentinel data available free of charge and supplementary technical and geodata.
EFTAS methods detect ground movements
Surface movements can be observed over natural or untreated bog areas, because bog bodies have the ability to swell or shrink due to their structure. The methods developed by EFTAS for the differential evaluation of satellite-based RADAR images with synthetic aperture make it possible to observe these surface movements in the millimetre range.
Within the framework of the project, clear statistical correlations between soil moisture and ground movements could be demonstrated with the help of RADAR observations at various locations in peatlands. Thus, with the help of the processes developed by EFTAS, it will be possible in the future to make statements on soil moisture and the degree of rewetting of peatland soils over large areas.
Further information on the remote sensing-based processes can be found here:
https://bewamo.de/einsatz-von-fernerkundung
BEWAMO project website with geotool
In the "BEWAMO" project, an assessment tool for categories of conservation value and for remote sensing-based monitoring of agriculturally used peatlands was developed. The Humboldt University Berlin, the Christian Albrechts University Kiel, the Thünen Institute and the company EFTAS from Münster were involved. The project is part of a BMEL research initiative on climate protection and climate adaptation in agriculture.
A good overview is provided by the website https://bewamo.de implemented by EFTAS, which contains information about the project and an interactive demonstration of the tools developed in BEWAMO. The map portal can be accessed at https://bewamo.de/eftas-geoportal.
[12.04.2023] Climate protection through peatland conservation
BEWAMO project completed: Assessment and monitoring of peatlands … [read more]

26.04.2023Water monitoring for the Wupperverband.
Remote sensing holds great opportunities for water management. read more26.04.2023Water monitoring for the Wupperverband.
Remote sensing holds great opportunities for water management.
The Wupperverband (a public water management association) has been responsible for water management tasks in the 813 km² catchment area of the Wupper for almost 100 years. Today, the association maintains 14 dams, 11 sewage treatment plants, numerous rainwater and flood retention basins as well as about 2,000 kilometres of rivers and streams.
In recent years, extreme hydrological events, such as floods and heavy rainfall, but also heat and dry periods, have increasingly occurred. These pose new challenges for the Wupperverband in terms of raw water supply and flood protection.
Monitoring of dams
Sentinel data and Copernicus services can usefully support water management processes at the Wupperverband. One important aspect is the continuous monitoring of the catchment areas of the Wupper as well as the dams, which serve as drinking water reservoirs, among other things.
An important indicator for assessing water quality is the chlorophyll concentration. Land use, vegetation density and the vitality of the surrounding forests continue to play an important role in monitoring the catchment area of the Wupper. These have an impact on possible substance inputs into the flowing waters and dams.
Sentinel data as a basis
Since March 2022, EFTAS has been producing weekly detailed maps for the Wupperverband area with information on the current chlorophyll-a values in the near-surface water layers based on Sentinel-2 data. These show any hotspots that may be present and enable a comparison of the situation of all dams at one point in time.
At the same time, EFTAS calculates the vegetation density (fractional vegetation cover) in the catchment area of the Wupper, so that differences in vitality between years and over the course of the year can be determined. The Sentinel data, which is available free of charge, is also used to calculate vitality indices such as the NDVI.
Vision Digital Twin
The use of satellite data provides the Wupperverband with additional data. The regularly determined chlorophyll values serve as an early warning system and can provide important information on the purity of the raw water (the basis for drinking water treatment).
In the future, the Wupperverband aims to further develop environmental monitoring into a "digital twin" for the Wupper catchment area by further digitalising data, algorithms and processes. Real-time information can support planning, decision-making and control processes. Examples include water supply management adapted to climate change, modern forecasting models for dams or warnings in the event of flood danger or unauthorised discharges.
[26.04.2023] Water monitoring for the Wupperverband.
Remote sensing holds great opportunities for water management. … [read more]
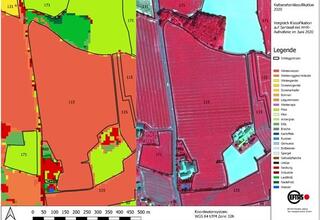
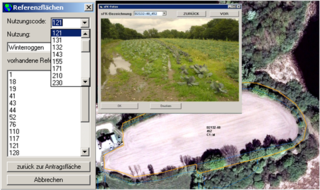
08.02.2023EFTAS develops AI for agricultural subsidy control.
Photo app and artificial intelligence facilitate subsidy area applications. read more08.02.2023EFTAS develops AI for agricultural subsidy control.
Photo app and artificial intelligence facilitate subsidy area applications.
For years, EFTAS has taken over the remote sensing-based control of agricultural subsidy areas for many European countries as part of the Integrated Administration and Control System (IACS).
A current EU reform now requires a new area monitoring by the agricultural administrations of the countries. Previously, subsidy applications from around five percent of farms were checked. Starting this year, a check of all applicants must be carried out.
Satellite images for automated agricultural monitoring
The basis for an efficient check is provided by sentinel images from the European Copernicus program, which are available free of charge. Using time series of these satellite images, all areas are automatically checked for compliance with certain eligibility requirements, conditions and obligations. State-of-the-art technologies are used to evaluate the data stored on cloud systems with artificial intelligence. This is done by comparing the automated real land uses with the information provided by the farmers and either confirming the applications or indicating discrepancies.
Full automatic control is currently still limited by some technical constraints. Some uses cannot be distinguished in the satellite data, and the resolution of the satellite data is currently not sufficient especially for narrow areas. In these cases, the farmer will have to submit a digital photo of his land in the future.
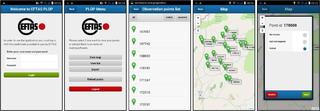
EFTAS CropANALYZER - photo evaluation by AI
The digital photos of the application areas can be taken with a photo app, which was developed by the company GI Geoinformatik GmbH. Based on its many years of experience with field mapping and voucher photos, EFTAS has developed an application that allows automated evaluation of these images.
The EFTAS-CropANALYZER consists of a database with over 50,000 photos of agricultural uses and an artificial intelligence that automatically determines the depicted use. The smartphone's position data stored with the photo can also be used to determine the photographer's location and line of sight and match it with the location of the land in question.
From now on, the EFTAS CropANALYZER can be tested. The prototype web application allows the free use of an artificial neural network to determine agricultural crop types with photos from the field.
Test EFTAS CropANALYZER here:
[08.02.2023] EFTAS develops AI for agricultural subsidy control.
Photo app and artificial intelligence facilitate subsidy area applications. … [read more]
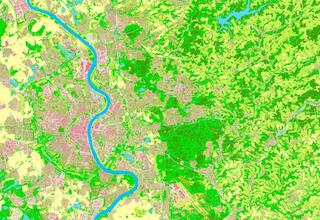
21.06.2023New: Technical Operating Unit "Land Cover"
EFTAS provides basic data derived from Copernicus data read more21.06.2023New: Technical Operating Unit "Land Cover"
EFTAS provides basic data derived from Copernicus data
Precise information on the cover of the Earth's surface forms the basis for most environmentally relevant questions, be it on the degree of soil sealing, landscape planning, climate simulations or reporting to the European Commission.
To answer these questions, the Federal Government and the Federal States of Germany have now set up the joint Technical Office "Land Cover" (Technische Betriebsstelle „Landbedeckung“). The Technical Operating Agency is managed by the Cologne District Government, Geobasis NRW (Bezirksregierung Köln, Geobasis NRW) and the Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy (Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie). The state agency IT.NRW (Landesbetrieb IT.NRW) is responsible for the cross-state administration and coordination of the IT infrastructure.
Evaluation of Copernicus data as a basis
The data sets on land cover are provided by the Central Office of Geotopography (ZSGT) (Zentrale Stelle Geotopographie (ZSGT)) in an up-to-date, geometrically accurate and demand-oriented manner for the entire federal territory. The satellite data of the European Copernicus programme as well as the aerial photographs available at the federal states are mainly used to calculate the land cover. These remote sensing data sets are evaluated using automation-supported classification procedures and artificial intelligence methods.
The basis for deriving land cover was developed within the Cop4ALL NRW project (Copernicus for ATKIS, ALKIS and land cover / Copernicus für ATKIS, ALKIS und Landbedeckung), in which the companies EFTAS and VertiGIS are involved as project partners.
Remote sensing procedure Cop4ALL NRW in operation
With Cop4ALL NRW, the land cover for North Rhine-Westphalia was derived for the first time in a comprehensive and fully automated manner on the cut-off date of 1 April 2022. The dataset is freely available via services in accordance with the Open Data principle.
The land cover in NRW can be accessed via the following link https://lmy.de/rQqLACPM (section of Cologne and surroundings).
EFTAS awarded contract for Cop4ALL-DE
The Cop4ALL NRW procedure is to be further developed in order to derive the land cover for the whole of Germany in the future. The procedure will be called Cop4ALL-DE in future. EFTAS has been commissioned to carry out this technical development.
With Cop4ALL-DE, the land cover of all of Germany will be recorded for the first time according to uniform specifications in a high geometric resolution and updated at regular intervals. The aim is to offer a nationwide land cover dataset to the public in summer 2024.
[21.06.2023] New: Technical Operating Unit "Land Cover"
EFTAS provides basic data derived from Copernicus data … [read more]

29.08.2023LUCAS & EMBAL on the home straight.
European field surveys completed. read more29.08.2023LUCAS & EMBAL on the home straight.
European field surveys completed.
EFTAS was again involved in two major European field surveys: LUCAS and EMBAL!
The surveys for long-term monitoring of landscape development and biodiversity of agricultural landscapes are mainly organised and carried out by EFTAS.
EMBAL - Mapping in 27 countries
The European Monitoring of Biodiversity in Agricultural Landscapes (EMBAL) was a pilot project in 2018, collecting harmonised biodiversity data across different EU member states.
In 2022, EMBAL mapping was carried out for the first time across Europe using a representative sample of 3.000 landscape sections (plots) of 500 x 500 m in size. This year, the second mapping was carried out, in which the same plots were surveyed a second time in order to detect monitoring effects. The on-site surveys included detailed plot and vegetation surveys as well as photo documentation.
EFTAS was responsible for the coordination of over 90 mappers who travelled from Cyprus to Finland between March and August in both years. The mappers were prepared for their task with training courses. All data collection was digital and mobile with an EMBAL app customised by EFTAS.
Remote sensing data processing
The base for the mapping is formed by aerial photographs that have already been pre-processed by EFTAS for the 3,000 plots according to certain criteria. Landscape elements such as hedges, ditches, groves as well as arable and grassland plots have already been identified and digitised using established processes. A refinement of these data is carried out by the mappers in the field. They also add photos and notes and record a variety of parameters. At EFTAS, all data is currently aggregated and stored in a database in a structured way. The approximately 170,000 photos supplied document the parameters recorded and are included in the evaluation. The results of the EMBAL procedure will be comprehensively analysed in a next step, so that important statements regarding biodiversity and its development can be made EU-wide.
LUCAS - Mapping land cover in Europe
For the LUCAS project, the mappers for EFTAS were also on the road in many European countries. The Statistical Office of the European Union (EUROSTAT) had once again commissioned the Münster-based company to carry out the survey.
LUCAS is the abbreviation for "Land Use and Coverage Area frame Survey". In addition to the regular collection of land cover and land use data, soil samples are also taken and grassland parameters are recorded during the on-site mapping. EFTAS has been regularly commissioned with the surveys within the framework of LUCAS since 2001 and also coordinated a Europe-wide network of mappers and partner companies for the current survey, provided training and ran the back office for the support of the field staff. With the start of the field survey, the internal quality control and the preparation for delivery to the external quality control of EUROSTAT then also played an essential role.
EMBAL and LUCAS are coordinated both spatially and in terms of content. LUCAS is a point survey, and this point network also serves as the centre point for the EMBAL plots. In terms of content, the nomenclatures are aligned to allow comparison and complementation of both datasets.
[29.08.2023] LUCAS & EMBAL on the home straight.
European field surveys completed. … [read more]

31.08.2023Forest planning 4.0 in the forest planning process.
Bavarian State Forest Administration (Bayrische Staatsforsten) pushes digitalisation. read more31.08.2023Forest planning 4.0 in the forest planning process.
Bavarian State Forest Administration (Bayrische Staatsforsten) pushes digitalisation.
The forest is becoming increasingly digital. In forestry, innovative processes offer great potential and support in particular the value chain from timber production to harvesting to transport to the processing industry.
The Bavarian State Forest Administration therefore wants to optimise the adaptation of forest management processes and their IT support in the future in order to achieve a higher degree of digitalisation and automation and at the same time improve data quality. Remote sensing data and products play an important role in this.
New "Forest Planning 4.0" ("Waldplanung 4.0") project in Bavaria
One goal of the five-year project "Forest Planning 4.0 - Forest Remote Sensing" („Waldplanung 4.0 – Forstliche Fernerkundung“) of the Bavarian State Forest Administration is the automated derivation of specialised forestry products from remote sensing data. The project partners EFTAS, AVT, GI Geoinformatik and Materna will develop innovative methods and products that will be integrated into regular operations.
The focus of the developments is on optimising forest management. Furthermore, the reaction to major damage events is to be supported with remote sensing data and analysis methods.
Processing of forestry products
EFTAS is contributing its many years of expertise in the field of remote sensing to the project. The Münster-based company is responsible, among other things, for the further processing of the remote sensing data used and is developing methods and algorithms for deriving new specialist forestry products. Products for analysing vegetation height and structure, tree species classifications and forest structure maps are planned, which will be generated using aerial images, laser scan data, satellite image time series and modern AI algorithms. These specialised products are integrated into the forest inventory process to increase the efficiency of forest management.
In the case of damage events, for example due to storms, it is planned to record affected areas as needed within the framework of a "fast response" mapping. For this purpose, EFTAS will create corresponding maps of damaged areas at short notice on the base of remote sensing data and thus support the decision-making processes at the Bavarian State Forest Administration. The aim is a standardised and rapid assessment of the damage situation that has occurred.
[31.08.2023] Forest planning 4.0 in the forest planning process.
Bavarian State Forest Administration (Bayrische Staatsforsten) pushes digitalisation. … [read more]

20.09.2023We feed your digital twin.
EFTAS at Intergeo 2023 in Berlin. read more20.09.2023We feed your digital twin.
EFTAS at Intergeo 2023 in Berlin.
The leading international trade fair for geodesy, geoinformation and land management will take place from 10 to 12 October in Berlin. With the motto "We feed your digital twin." we are placing our focus this year on the topic "digital twins". Our feed for your digital twin includes, for example:
- High-resolution (3D) baseline data.
- Remote sensing-based monitoring data and derived change information.
- In situ data, collected in the field (validation, ground truthing, mapping).
We show demonstrators such as:
3D City Daten (3D City Data): Sealing mapping and city models for municipal tasks.
Cop4ALL: Copernicus for ATKIS, ALKIS and land cover. AI-supported derivation of land cover data from sentinel images and orthophotos including change detection procedures for data updates.
Wald 4.0 (Forest 4.0): Forest management and damage monitoring with remote sensing and AI.
LUCAS & EMBAL: Europe-wide surveys for long-term monitoring of landscape development and biodiversity in agricultural landscapes.
Find out more at booth D1.041 in hall 1.2 and make an appointment with us!
By email at intergeo@eftas.com or by phone at +49 251 133070.
Your guest card will be sent to you immediately.
Another note for participants of the Intergeo conference:
On the first day of the event, Dr Andreas Müterthies will take part in the panel discussion „Satellitenfernerkundung in der Geoinformationsverwaltung" („Satellite-based remote sensing in geoinformation administration"). He will speak on the topic: "Innovations through AI".
Room BETA 8+9, / Tuesday, 10/10/2022 / 3:30 - 4:30 pm.
[20.09.2023] We feed your digital twin.
EFTAS at Intergeo 2023 in Berlin. … [read more]

10.06.2022LUCAS - A EUROPEAN WIDE MAPPING PROJECT.
EFTAS was contracted for 2022 LUCAS Survey. read more10.06.2022LUCAS - A EUROPEAN WIDE MAPPING PROJECT.
EFTAS was contracted for 2022 LUCAS Survey.
EFTAS was contracted for 2022 LUCAS Survey.
By decision of the Statistical Office of the European Union (Eurostat), EFTAS was contracted to carry out the LUCAS Survey in 2022 in the countries of lots 2, 3 and 4.
In addition to the regular collection of land cover and land use data, on-site mapping also involves soil sampling and the collection of grassland parameters.
Introductory information on LUCAS can be found here: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/de/web/lucas/overview
Further links:
[10.06.2022] LUCAS - A EUROPEAN WIDE MAPPING PROJECT.
EFTAS was contracted for 2022 LUCAS Survey. … [read more]

10.12.2021Job Offer:
Surveyors for LUCAS field surveys 2022. read more10.12.2021Job Offer:
Surveyors for LUCAS field surveys 2022.
We are looking for surveyors for LUCAS field surveys 2022 in:
- Finland
- Denmark
- the Netherlands
For details, see Careers.
[10.12.2021] Job Offer:
Surveyors for LUCAS field surveys 2022. … [read more]

19.11.2021Advance notice:
call for surveyors (2022). read more19.11.2021Advance notice:
call for surveyors (2022).
We are looking for freelance experts for agri-environmental field surveys.
[19.11.2021] Advance notice:
call for surveyors (2022). … [read more]

07.10.2021Press release: NEXT [...] fulfill expectations.
Project for new exploration techniques successfully completed. read more07.10.2021Press release: NEXT [...] fulfill expectations.
Project for new exploration techniques successfully completed.
On the successful completion of the Horizon 2020 project NEXT (New Exploration Technologies), the Geological Survey of Finland has written a press release (see download).
In the project, EFTAS had major parts in the conception of the Satellite Image Crawler (SIC) as a universal software tool for data search, acquisition, analysis, storage and post-processing, as well as in the development of specific remote sensing-based data products for mineral exploration and environmental monitoring.
Details of EFTAS' work in NEXT can be found on the NEXT hompage in the post REMOTE SENSING | Satellite-imagery derived products.
[07.10.2021] Press release: NEXT [...] fulfill expectations.
Project for new exploration techniques successfully completed. … [read more]

15.09.2021Monitoring for the protection of biodiversity.
EMBAL - Duet with LUCAS? read more15.09.2021Monitoring for the protection of biodiversity.
EMBAL - Duet with LUCAS?
Biodiversity is declining worldwide.
National and international policymakers are trying to counter this alarming trend with various instruments, e.g. through the United Nations' sustainable development goals, the EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2020 or components of the EU's Common Agricultural Policy.
Finding the right actions is not trivial due to the complex interdependencies between natural values, ecosystem services and socio-economic factors.
To objectively monitor and assess the development of biodiversity and the effects of actions at European level, robust data are needed.
With the European Monitoring of Biodiversity in Agricultural Landscapes (EMBAL), an approach was presented in 2018 that allows for the creation of harmonised data on biodiversity across the EU member states.
EMBAL is based on field measurements of landscape sections (so-called “plots”) with a size of 25 ha (500 x 500 m). The survey follows a threefold approach: (1) an area survey, in which parameters on agricultural parcels and landscape elements are recorded, (2) a vegetation survey based on 4 transect lines, in which structural parameters of vegetation and key species are assessed, and (3) a photo documentation for visual characterisation of the parcels and transects and for tracking changes over time.
The EMBAL method will be further optimised in 2020/21 by a consortium consisting of EFTAS, the Institute of Agroecology and Biodiversity (IFAB) and the Federal Environment Agency Austria (EAA).
A key strategy for EMBAL optimisation is to focus the survey on easily identifiable parameters such as the occurrence of flowering key species groups and ecological indicators that go beyond purely botanical aspects. By standardizing the data collection, this approach makes it possible to increase the accuracy of the results and to expand the group of potential surveyors with the appropriate qualifications for large-scale surveys.
With this approach, the integration of the EMBAL survey into the European in-situ survey framework LUCAS and the LUCAS Grassland Module 2018 is also a conceivable perspective.
The revised and extended survey method was tested with pilot surveys from April to June at about 250 plots in Germany, Spain, Romania and Austria.
As download you can find here the EMBAL poster from the symposium of the European Grassland Federation.
[15.09.2021] Monitoring for the protection of biodiversity.
EMBAL - Duet with LUCAS? … [read more]

29.07.20212006, 2012 and 2018.
Natura 2000 Copernicus Hotspot Monitoring completed. read more29.07.20212006, 2012 and 2018.
Natura 2000 Copernicus Hotspot Monitoring completed.
With the digital final meeting in early summer we officially completed the Copernicus Natura 2000 project "Copernicus Hotspot Monitoring Services - Production of Very High Resolution Land cover / Land use datasets in selected Natura 2000 sites. Reference year 2018 including change layer 2012-2018" officially closed (see also Remote sensing and collaboration.).
Under the sign of Corona it was an intense time, which was not only instructive due to the new change mapping approach, but also let us develop innovative methods of collaboration from the home offices.
Therefore, we are happy that we were able to lead the project to a super result. The very good cooperation with the cooperation partners and the EEA (European Environment Agency) contributed to this.
The European Commission has published a detailed post on the data set and first evaluations, which can be found here as a download or at:
[29.07.2021] 2006, 2012 and 2018.
Natura 2000 Copernicus Hotspot Monitoring completed. … [read more]

12.07.2021Publication: Soil Moisture Monitoring.
Advanced DInSAR approach presented at ISPRS. read more12.07.2021Publication: Soil Moisture Monitoring.
Advanced DInSAR approach presented at ISPRS.
At the last ISPRS Congress, we presented results on the use of Advanced DInSAR for soil moisture monitoring. The paper has been published in the ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences for the 2021 edition of the XXIV ISPRS Congress.
Yang, C. H. and Müterthies, A.: MONITORING OF TIME-SERIES SOIL MOISTURE BASED ON ADVANCED DINSAR, ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci., V-3-2021, 51–55, https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-annals-V-3-2021-51-2021, 2021.
https://www.isprs-ann-photogramm-remote-sens-spatial-inf-sci.net/V-3-2021/51/2021/
[12.07.2021] Publication: Soil Moisture Monitoring.
Advanced DInSAR approach presented at ISPRS. … [read more]

01.07.2021Take For(e)stCARe.
System integration and more AI for forest monitoring. read more01.07.2021Take For(e)stCARe.
System integration and more AI for forest monitoring.
Bark beetles, drought damage, rising timber prices - forestry issues like these are unfortunately very relevant.
That's why satellite image analysis is currently in high demand, enabling regular, cost-effective and rapid monitoring of forest areas.
The methodology is already in operational use.
We are currently also integrating it into the update of the GIS platform Waldinfo.NRW to optimize and expand satellite-based calamity area monitoring.
In order to be able to use the method faster and more universally in the future for the detection of illegal clearing as well as for the recording of climate-induced forest damage and support of reforestation measures, we are now optimizing it at two points using AI approaches:
- sufficiently representative training data
- cloud-related data gaps
Artificial neural networks require a great amount of training data. In order to be able to use representative training data in the necessary quantity and quality, we are investigating transfer learning techniques, in particular domain adaptation and so-called label noise tolerant methods, which can detect and discard error-prone training data or transform it into a suitable form.
Cloudy situations can significantly limit the rapid availability of suitable optical satellite data. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) provide a way to simulate missing optical data from radar data. The principle is based on joint training of optical and radar data in cloud-free areas. Sentinel 1 data, among others, are used here.
The project for the activities is called ForstCARe. The acronym stands for "Forestry (in German: Forstwirtschaftlicher) Copernicus-based Assistance Service - Reduction of reference data requirements and fusion of sensor data to fill cloud-related data gaps for classification using artificial intelligence (AI)." It is funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy via DLR (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V.).
The Institute of Photogrammetry and GeoInformation (IPI) at Leibniz Universität Hannover is involved in the project as a development partner, as are the Landesbetrieb Wald und Holz NRW and the Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE) from Brazil as associated partners.
[01.07.2021] Take For(e)stCARe.
System integration and more AI for forest monitoring. … [read more]

16.06.2021Ground Movements.
Cost-efficient monitoring with AI and customized data. read more16.06.2021Ground Movements.
Cost-efficient monitoring with AI and customized data.
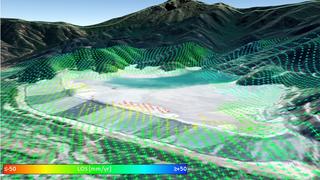
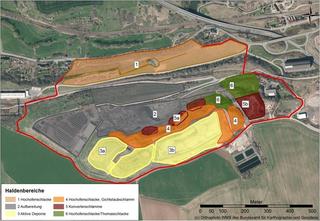
Active mining or post-mining responsibility - the monitoring of mining-affected areas must be ensured over long periods of time, often associated with considerable costs. An important process is the monitoring of ground movements that can result from mining activities or their consequences. Early detection of changes can help to avoid or reduce damage through timely preventive measures.
EFTAS offers efficient, continuous monitoring of ground movements based on remote sensing. An important basis for the automated monitoring is radar interferometry, which allows almost daily measurements of changes in the earth's surface. The results, together with other data (e.g. mining surveying information on fissures, other geo-information as well as optical satellite data and in-situ data), enable precise, cost-efficient and permanent monitoring of ground movements caused by mining. This procedure ensures a reduction of the time-consuming controls through the manual on site surveying.
Use Case Ruhr area (Ruhrgebiet)
With the end of active coal mining in North Rhine-Westphalia, a lot of post-mining tasks in the Ruhr area have to be managed. EFTAS is part of a project consortium that develops different measurement methods and systems to detect ground movements in the Ruhr area. Standard radar interferometry methods such as SBAS or PSI are very important for an automated monitoring. To optimize the results, EFTAS integrates additional information (e.g. in-situ data and optical satellite data) into the automated analysis process. Ground movements relevant for the risk assessment are filtered by an AI-supported reduction method to provide in this form a meaningful basis for an efficient monitoring system.
Mining, water, gas and oil - The causes of ground movements are manifold
Whether uplift, subsidence or sliding - surprising and sudden movements of the earth surface can pose a great danger to people and cause extreme damage. For prevention, the possible causes must be continuously monitored. Among the most common are:
- Mining activity
- Oil and gas activities
- Subsidence due to groundwater exploitation
- Subsidence due to natural or accelerated consolidation
- Engineering works and infrastructures
- Landslides in mountain environments
- Motion in volcanic areas
EFTAS monitoring can be used in almost all cases.
Monitoring expertise from Münster
Ground motion monitoring based on radar data in combination with optical satellite data and results of terrestrial campaigns using artificial intelligence is one of the core competences of EFTAS.
Our methods are constantly evolving to improve the application in mining and energy industry processes monitoring infrastructures such as pipelines, tailings or cavern storage facilities. . Examples are current R&D projects such as:
- i2Mon: Development of an integrated monitoring service for the detection, assessment and prediction of ground and slope movements resulting from mining activities (see also: i2MON - Mine Monitoring.)
- STINGS: The tailings monitoring service based on remote sensing data and ground-based sensor information provides a monitoring system for safety-relevant aspects such as stability and material release of tailings dams (see also: STINGS tailing monitoring.)
The extraction of oil and gas from the ground changes the pressure conditions in the reservoir rock. This can lead to subsidence at the surface, but also to small earthquakes due to stress discharges. Elsewhere , natural gas or other reserves are stored underground. These so-called cavern storage facilities and pore storage facilities are indispensable for gas supply and the operation of distribution networks. Whether production or storage - safety under and above ground must be guaranteed at all times. In addition to spaceborne remote sensing methods, EFTAS also uses drones with thermal imaging cameras to detect leaks at an early stage.
- Cavern monitoring in the context of salt extraction: monitoring of ground movements incl. change detection of vegetation vitality
- KaMonSys: Monitoring system for the plant and supply security of cavern storage facilities using satellite and drone data (see also: Efficient monitoring of cavern storage facilities.)
Another cause of soil movement is drainage. This is evident, for example, in the intensive use and deep drainage of agriculturally used peat soils. The consequences include severe soil degradation and reduced carbon storage capacity. Monitoring based on Sentinel-1 and -2 data as well as in-situ sensors enables the detection of soil movements and conclusions on the peatland landscape condition.
- BeWaMo: Assessment tool for categories of conservation value and for remote sensing-based monitoring of agriculturally used peatlands
[16.06.2021] Ground Movements.
Cost-efficient monitoring with AI and customized data. … [read more]

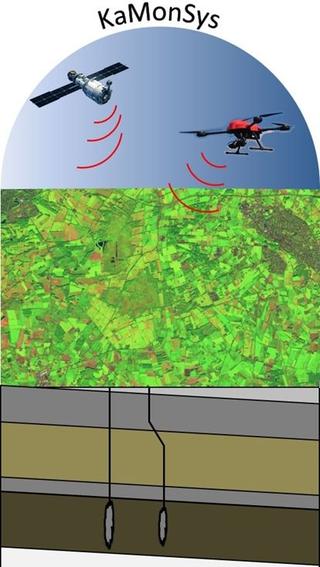
02.06.2021Efficient monitoring of cavern storage facilities.
KaMonSys integrates satellite and copter data. read more02.06.2021Efficient monitoring of cavern storage facilities.
KaMonSys integrates satellite and copter data.
Whether defects, accidents or sabotage - the safety of underground storage and supply facilities for natural gas and other resources but also the associated above-ground technical facilities must be guaranteed at all times. It is the responsibility of the operators to detect possible leaks early and reliably. This is the only way to prevent gaseous emissions and any resulting damage to people and nature.
Current procedures are mainly based on visual inspections on site, helicopter flights to measure methane concentrations in the atmosphere, and walk-throughs or drive-throughs with gas detection equipment. In widely spread facilities, these inspections are time-consuming, personnel-intensive and cost-intensive.
Related to this background, EFTAS is currently developing an automated monitoring system for cavern storage facilities in the Westmünsterland region with partners from industry and academia that combines geoscientific analyses, both in-situ and laboratory methods, with remote sensing methods. The "KaMonSys" project, monitoring system for the plant and supply security of cavern storage facilities using satellite and copter data, is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research and will run until mid-2022.
In addition to continuous monitoring of technical plant functions and geological underground and subsurface parameters, various satellite data from the Copernicus program are being evaluated. If irregularities occur during this permanent analysis, an autonomously flying copter is used. The device is equipped, among other things, with a thermal imaging camera and can should detect uncontrolled gas leaks with high precision on the basis of thermal images. The characteristic temperature differences in the environment but also on the surfaces of the technical infrastructures are to be made visible with high precision at pixel level and thus potential leaks or leakages can be localized.
The novel monitoring system serves the highest imperatives of the cavern and pore storage industry: the reliability of surface and underground technical facilities as well as the security of supply through the provision of the raw materials placed underground. For this purpose, methods of remote sensing in the field of copter and satellite-based technology are combined with analyses and evaluations of open geodata, mining crack works and site-specific safety information. The application is initially aimed at operators of pore and cavern storage facilities. However, with little adaptation effort, the results are transferable to numerous other application areas that work with gases, gas-technical plants and volatile hazardous substances.
photo: Stefanie Krause
[02.06.2021] Efficient monitoring of cavern storage facilities.
KaMonSys integrates satellite and copter data. … [read more]

25.05.2021Fire (danger) watcher for associated green.
Cloud and AI-based Copernicus service CCFireSense. read more25.05.2021Fire (danger) watcher for associated green.
Cloud and AI-based Copernicus service CCFireSense.
There are people who work honorably as fire watchers. For the Regionalverband Ruhr, fire watchers use binoculars to spy on the Haard for forest fires from high towers during dry periods.
The satellites of the European Copernicus program are also called watchers: namely Sentinels. In the new CCFireSense project, they also act as fire watchers in a sense. However, not to detect fires that are already burning, but to prevent fires. So here they are more like fire danger watchers. However, the project is not only about large forest areas, but also explicitly about the prevention of fires along roads and railways.
The subtitle to the project is therefore:
Cloud-based Copernicus service for monitoring and fighting forest and wildfires along transport infrastructures.
CCFireSense is a multi-level satellite-based warning service that uses automated vegetation monitoring to detect growing fire danger along transportation infrastructures and in the surface. A conceptually integrated drone-based in-situ component complements the system.
The project is being carried out by the Institut der Feuerwehr Nordrhein-Westfalen (IdF NRW). EFTAS was contracted by IdF NRW to support with the necessary expertise for remote sensing as well as cloud and machine learning based data analysis.
[25.05.2021] Fire (danger) watcher for associated green.
Cloud and AI-based Copernicus service CCFireSense. … [read more]

20.05.2021BEWAMO & EMBAL.
EFTAS at the Symposium of the European Grassland Federation. read more20.05.2021BEWAMO & EMBAL.
EFTAS at the Symposium of the European Grassland Federation.
The 21st Symposium of the European Grassland Federation (EGF) from May 17-19 addressed an - quote from the homepage - "innovative and dynamic research area - namely the application of remote sensing for improving the assessment of biomass, forage quality and ecosystem services of grasslands".
We used the stage to provide insights into two of our R&D projects:
- BEWAMO: Wide-area monitoring of soil moisture in peatlands using Sentinel-1 images
- EMBAL: European Monitoring of Biodiversity in Agricultural Landscapes
[20.05.2021] BEWAMO & EMBAL.
EFTAS at the Symposium of the European Grassland Federation. … [read more]

11.03.2021Mono Earth Observation.
"Dual" Consultancy Project for UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. read more11.03.2021Mono Earth Observation.
"Dual" Consultancy Project for UNESCO Biosphere Reserve.
Monotemporal remote sensing is known, stereophotogrammetry is known, but what should Mono Earth Observation (EO) be?
It's simple. Mono is the name of the river which´s delta belongs to a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve that was the central subject of the project "Consultancy on the application of satellite earth observation for coastal and marine monitoring" on behalf of the German Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ).
UNESCO biosphere reserves are model regions in which sustainable developments in ecological, economic and social respects are realized in an exemplary manner. For such regions, the acceptance and support of the local people are very important factors.
Can GeoIT support participative approaches? This question was investigated in the project by evaluating and demonstrating possibilities of using satellite remote sensing and GIS tools.
Beyond the river name, however, there was little that was "mono" in the project.
- Because the Mono Delta is transboundary, TWO states were involved: Benin and Togo.
- In charge of the consulting were TWO companies: EFTAS and Brockmann Consult.
- The alignment of the project to the needs of the local stakeholders was based on TWO elements: the so-called Fact Finding Mission to evaluate the technical and organizational situation and the Stakeholder Workshop to exchange information about existing suitable international EO programs, usable analysis applications and relevant satellite systems.
- In order to demonstrate in detail the technical possibilities and practical benefits for the Biosphere Reserve, TWO Use Cases were identified and elaborated: Water Quality and Sustainable Land Use.
The actual GeoIT approaches and results are of course beyond this dual enumeration mode, but shall not be further elaborated here.
In the final consideration again TWO aspects are important:
As far as local settings are really addressed, technology being adapted and capacities being built, GeoIT offers excellent opportunities to analyze and demonstrate the impact of socio-economic conditions on the environment and in this way to develop solutions for a more sustainable coexistence of humans and nature.
In addition to the time and resources required for the operational implementation of GeoIT tools, there is one fundamental pre-condition for this: the political will to use this technology must be felt by all those involved and must be the guideline for all stakeholders.
[11.03.2021] Mono Earth Observation.
"Dual" Consultancy Project for UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. … [read more]

01.12.2020Projectflyer: Bush Information System.
A modern decision support tool. read more01.12.2020Projectflyer: Bush Information System.
[01.12.2020] Projectflyer: Bush Information System.
A modern decision support tool. … [read more]
11.08.2020Publication: Precipitation causes soil movement.
ISPRS paper about prediction model using ADInSAR. read more11.08.2020Publication: Precipitation causes soil movement.
ISPRS paper about prediction model using ADInSAR.
Our paper "Modelling and Prediction of Precipitation and Soil Movement Based on ADInSAR" is now available on ISPRS Annals.
Evaluating soil movement related to rainfall is needed for geologic and hydrologic applications. In principle, the soil body swells and shrinks depending on soil type, precipitation rate, moisture content, and drainage rate. We have developed a predictive model to estimate precipitation from DInSAR-derived soil movement, and vice versa. Our test in Tinner Dose using Sentinel-1 data shows the prediction accuracy for precipitation is 14 mm (mean error rate 12%) and it amounts 12 mm/yr for soil movement.
We will dig at this topic along with our geologic, hydrologic, and SAR projects.
Yang, C. H. and Müterthies, A.: MODELLING AND PREDICTION OF PRECIPITATION AND SOIL MOVEMENT BASED ON ADINSAR, ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci., V-3-2020, 179–184, https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-annals-V-3-2020-179-2020, 2020.
https://www.isprs-ann-photogramm-remote-sens-spatial-inf-sci.net/V-3-2020/179/2020/
[11.08.2020] Publication: Precipitation causes soil movement.
ISPRS paper about prediction model using ADInSAR. … [read more]

28.07.2020Web prototype "EFTAS CropAnalyzer" is on.
EFTAS enables Neural Network. read more28.07.2020Web prototype "EFTAS CropAnalyzer" is on.
EFTAS enables Neural Network.
A few months ago, our Business Geomatics report (in German) explained how we use artificial neural networks to analyse agricultural crop type photos. Now, we are happy to announce a new web application, that enables anyone to test this free prototype.
EFTAS Crop Analyzer: https://cropanalyzer.dev3.eftas.com/
The context:
EFTAS performs every year on-site observations of agricultural crops for more than 20,000 fields (see Trust is good but control is better!).
To conduct these field surveys, a comprehensive IT system is used that covers all aspects of digital field mapping: from logistical pre-planning, route planning, to routing and mapping via a smartphone app, including data synchronization between mobile app and central server storage and integration of a media database and Geographic Information System.
Also embedded is a Neural Network (NN) tool to automatically classify the collected field photographs into the most common thirteen crop types in Germany. Using this system, approx. 80% of all captured field photos can be automatically categorised with a very high confidence level and accuracy.
The EFTAS Crop Analyzer website offers now a free and direct access to the developed network for test and demonstration purposes. Upload your own crop type photo (out of the thirteen covered classes, check the FAQ section of the tool) and get the classification results back.
The website is available at https://cropanalyzer.dev3.eftas.com/ .
[28.07.2020] Web prototype "EFTAS CropAnalyzer" is on.
EFTAS enables Neural Network. … [read more]

13.07.2020We're on that.
EFTAS commits to digital Intergeo. read more[13.07.2020] We're on that.
EFTAS commits to digital Intergeo. … [read more]

20.05.2020About ADAM and evapotranspiration.
How green roofs influence the urban climate. read more20.05.2020About ADAM and evapotranspiration.
How green roofs influence the urban climate.
The analysis of the thermal effects of green roofs using urban climate modelling (ADAM for short) will be carried out with the same named project over the next two years for Essen and the area around it.
The consortium for this project, which is funded by the German Federal Environmental Foundation (DBU), is made up of the German Weather Service (DWD), the city of Essen, the German Association of Building Greening (BuGG) and EFTAS.
A central aspect is the determination of the cooling effect of green roofs, because vegetation usually has a higher albedo than conventional roofs and the air temperature is additionally reduced by the process of evapotranspiration.
EFTAS contributes the inventory of the green roof stock and potentially green roofs for the model calculations.
[20.05.2020] About ADAM and evapotranspiration.
How green roofs influence the urban climate. … [read more]
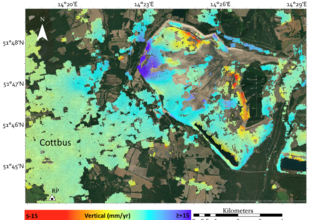
27.04.2020i2MON - Mine Monitoring.
First InSAR Result. read more27.04.2020i2MON - Mine Monitoring.
First InSAR Result.
The project Integrated Mining Impact Monitoring (i2MON) aims to develop a system chain to analyse mining-induced impact and deliver comprehensive information for decision-making. The monitoring system comprises terrestrial measurement and remote sensing, including levelling, GPS, LiDAR, UAV survey, and SAR interferometry.
Our first results have been published in Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences (PIAHS). This paper introduces our prototype of InSAR monitoring system. The test result from Sentinel-1 images depicts the surface deformation during 2018 at the deactivating open-pit coal mine owned by LEAG in Cottbus, Germany. We also discuss the current state, ongoing works, planned test sites in Poland, and how we integrate data from different sensors and approaches.
Yang, C.H. and Müterthies, A., 2020. Introduction of Integrated Mining Impact Monitoring - i2Mon Development Project. Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences, 382, pp. 225-229. (available at https://www.proc-iahs.net/382/225/2020/)
* i2MON is financed by European Commission - Research Fund for Coal and Steel (RFCS).
i2MON: https://i2monproject.eu/about-news
LEAG: https://www.leag.de/de/
[27.04.2020] i2MON - Mine Monitoring.
First InSAR Result. … [read more]
15.04.2020Remote sensing and collaboration.
Copernicus project starts in home office. read more15.04.2020Remote sensing and collaboration.
Copernicus project starts in home office.
In March 2020, the proven consortium of EFTAS, GAF and GeoVille has been commissioned by the European Environment Agency (EEA) to continue the Hot Spot Monitoring for Natura2000 (N2K) protected areas in order to extend the existing Local Copernicus Land Monitoring Service for the period 2018 (see Press release: EFTAS mapping for Copernicus N2K.).
The initial phase of the project was thus already affected by the Corona Pandemic. The kick-off meeting in Copenhagen was replaced by a video conference.
Of course, EFTAS also supports the measures to contain the spread of corona. The majority of the N2K team will therefore work in the home office until the situation has relaxed. We have adapted our ICT infrastructure in a very short time so that the N2K project can be carried out as planned by remote collaboration.
[15.04.2020] Remote sensing and collaboration.
Copernicus project starts in home office. … [read more]

25.02.2020Post-mining monitoring in the Ruhr area.
Kick-off for the proof of concept. read more25.02.2020Post-mining monitoring in the Ruhr area.
Kick-off for the proof of concept.
With the end of active hard coal mining in NRW, the Ruhr district is facing the challenge to cope with the possible effects in post-mining. To save energy costs, the artificially lowered deep pit water level is to be elevated. As a result of this level increase, the surface is expected to be uplifted in the coming years. The uplifts can lead to significant damage and restrictions of the public and private infrastructure. The detection of changes in the surface helps to avoid or at least reduce damage by taking early action.
With radar satellite data it is now possible to carry out large-scale monitoring even for the slightest ground movements. In the context of the risk management in post-mining mentioned above, this technology can be used for an early warning system.
The cities of Dortmund, Essen, Bochum, Duisburg and Mülheim an der Ruhr would like to implement such a system.
The association of cities has commissioned the project consortium consisting of DMT, EFTAS and the Research Institute of Post-Mining at THGA University to develop and operationalize a corresponding service infrastructure over the next two years.
As a proof of concept, the project consortium will examine the use of the DMT SAFEGUARD Monitoring Platform as a development basis for the following system functions:
- Provision of a web-based monitoring platform for the presentation of monitoring data and relevant geoinformation as a cloud service model (without the need for IT resources and software usage rights at the client)
- continuous monitoring of the surface in given spatial areas by means of satellite-based radar interferometry
- Operation of ground sensors (sensors on buildings and structures) as a further source of information for potential ground movements of the surface
- Inclusion of further geoinformation relevant to post-mining (including risk map of old mining areas) and technical expertise
EFTAS contributes to the continuous monitoring of the earth's surface in predefined spatial areas using satellite-based radar interferometry by analyzing Sentinel-1, TerraSAR-X and PALSAR-2 data.
The kick-off for the proof of concept took place in mid-February at DMT in Essen.
[25.02.2020] Post-mining monitoring in the Ruhr area.
Kick-off for the proof of concept. … [read more]

27.01.2020Eleven good years.
RapidEye era comes to an end. read more27.01.2020Eleven good years.
RapidEye era comes to an end.
[27.01.2020] Eleven good years.
RapidEye era comes to an end. … [read more]

22.11.2019UN-SPIDER Conference:
Space-based Solutions for Africa. read more22.11.2019UN-SPIDER Conference:
Space-based Solutions for Africa.
I was in Bonn from 6 to 8 November. UN-SPIDER had invited to the international conference "Space-based Solutions for Disaster Management in Africa: Challenges, Applications, Partnerships". Participants from more than 20 countries were present, many of them from Africa. And that's exactly what made the event so interesting. Because many African participants had active program contributions and created so a decided picture of the use and need situation of GeoIT in the disaster management cycle in practice. On the one hand concerning the range of applications for disaster scenarios such as floods, forest fires, landslides, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, but also phenomena that develop more slowly over time such as drought. On the other hand regarding the concrete possibilities of use for prevention, precaution, coping and subsequent recovery in the context of the infrastructures on site.
Luca Kleinewillinghöfer
[22.11.2019] UN-SPIDER Conference:
Space-based Solutions for Africa. … [read more]

22.10.2019No (GIS) desert.
National parks in Algeria. read more22.10.2019No (GIS) desert.
National parks in Algeria.
Many people associate Algeria with desert in their first thoughts. Not without good reason. 85% of the country belongs to the Sahara. But the remaining 15% are still as big as Germany. Of course in a land of this size there is a lot of nature and landscape worth protecting.
One approach to environmental protection, similar to what is practised in Germany, is the designation of national parks. Most national parks in Algeria are actually not found in the desert, but in the more Mediterranean regions in the north of the country. And, similar to the practice in in Germany, in the future the administrations of the national parks will be supported by a geo-information system (GIS).
The known GIS strengths with regard to recording, management, analysis and presentation of geodata are to be used to develop new protected areas, to manage existing parks even better and not least to improve the transfer of knowledge to the population in order to increase acceptance.
In El Kala National Park, a GIS has already been introduced by a project of the German Society for International Cooperation (GIZ).
Based on the experience gained in El Kala, EFTAS has been commissioned by GIZ to develop a consolidated guideline for GIS implementation and to implement this guideline as best practice with local stakeholders in the Mont Chenoua and Monts de l'Edough National Parks. The first hands-on training sessions have already taken place in Algeria. After the successful implementation, the decision makers and representatives of all national parks will be invited to a workshop to get an idea of the possibilities of the planned GIS infrastructures and to initiate the GIS rollout.
The framework for the project is the programme "Environmental Governance and Biodiversity" / "Gouvernance environnementale et biodiversité" (GENBI). It strengthens biodiversity management in Algeria and awareness of the importance of biological diversity and natural resources. GIZ coordinates GENBI and is supported in Algeria by the Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ) and the Ministère de l'Environnement et des Energies Renouvelables (MEER).
[22.10.2019] No (GIS) desert.
National parks in Algeria. … [read more]

30.08.2019Geo-IT in terms of international cooperation.
EFTAS at the GIZ exchange. read more30.08.2019Geo-IT in terms of international cooperation.
EFTAS at the GIZ exchange.
The German Society for International Cooperation (GIZ) invites to a professional exchange on 24 September 2019. The focus will be on technical trends and new players regarding the use of geoinformation and remote sensing in development cooperations.
In addition to new trends and topics, GIZ will also present special user cases from development cooperation.
Within the framework of an "Open Space" there will be the opportunity to present and engage in interesting discussions with and by participants.
EFTAS as a partner of GIZ in the GeoIT sector, especially in projects on the African continent, participates with the presentation of a broad application pool. The areas in demand are, for example, GIS applications and topics of agriculture, environmental and nature protection.
The professional exchange enables GIZ, EFTAS and other partners to best prepare for future projects for international cooperation.
See also: BIS in Namibia.
[30.08.2019] Geo-IT in terms of international cooperation.
EFTAS at the GIZ exchange. … [read more]

05.08.2019Set standards across scales.
EFTAS at the Intergeo 2019. read more05.08.2019Set standards across scales.
EFTAS at the Intergeo 2019.
Because cartographic scales are not really a criterion for remote sensing applications. Aerial and satellite images contain information for all scale levels. But you have to know how to extract the information. By comparing, composing and analyzing different data, remote sensing data can be scaled to regional issues.
We can do that. That's what we show.
On the Intergeo, for example, with the Bush Information System - BIS (BIS in Namibia.), which was then implemented for Namibia. The solution is the product of an international cooperation and combines sentinel data, terrestrial data acquisition, copter aerial photographs and WebGIS technology. The WebGIS service provides access to data that quantify the wood-like biomass per hectare based on satellite images.
Visit us in Stuttgart!
From 17 to 19 September 2019 you will find us on the areas F1.050 and -58 in hall 1.
[05.08.2019] Set standards across scales.
EFTAS at the Intergeo 2019. … [read more]

22.07.2019InSAR Monitoring in I2Mon.
Site Visit of Underground Mining in Poland. read more22.07.2019InSAR Monitoring in I2Mon.
Site Visit of Underground Mining in Poland.
Where coal is mined, ground and slope movements can occur. In the i2Mon project, a monitoring system is being developed which, through the integration of remote sensing techniques, should be able to detect these movements better than conventional terrestrial methods alone.
The core task of EFTAS is the integration of radar data of the satellite Sentinel-1, which will be analyzed with methods of the InSAR technique.
On July 2nd we visited the region at Krakau in Poland, where large underground mining activities are planned by Polska Grupa Górnicza (PGG). Extensive ground subsidence is expected. During our visit we exchanged views and information with project partners and stakeholders on site. The use of the new monitoring procedures is welcomed by the authorities and local residents. The results will serve the trustful relationship of the actors and affected parties. In Poland, the basis for good cooperation with PGG has been created. Now the first step is to map the ground situation with regard to the status prior to the start of the mining work.
I2Mon started in August 2018 and has a duration of 4 years. The project executing agency is RFCS (Research Fund for Coal and Steel).
[22.07.2019] InSAR Monitoring in I2Mon.
Site Visit of Underground Mining in Poland. … [read more]
![Publication: […] SAR IMAGES FOR MINING […].](https://www.eftas.de/upload/cache/phpThumb_cache_src741113525d7d39478dbf2bffff499bb2_par10b3db54d3de0e8f96ae456db75e7334_dat1562927053.jpeg)
21.06.2019Publication: […] SAR IMAGES FOR MINING […].
EFTAS in ISPRS Geospatial Week 2019. read more21.06.2019Publication: […] SAR IMAGES FOR MINING […].
EFTAS in ISPRS Geospatial Week 2019.
Radar remote sensing is becoming increasingly important. For example, we apply advanced InSAR techniques to monitor ground movements caused by natural processes or man-made reasons such as mining-induced subsidence.
From 10 to 14 June, we participated in the ISPRS Geospatial Week in Enschede, the Netherlands. With the contribution "Workable monitoring system based on spaceborn SAR images for mining areas - STINGS development project" we presented together with our international partners at the conference a workable system that uses spaceborn SAR images to monitor the stability of tailing dams at mining sites. The system was developed as part of the EIT Raw Material Project STINGS. We have received a lot of positive feedback and will continue to improve our system. Our goal is to launch an early warning system to prevent disasters such as dam failure.
Links:
ISPRS Geospatial Week: https://www.gsw2019.org/
Paper: https://www.int-arch-photogramm-remote-sens-spatial-inf-sci.net/XLII-2-W13/1951/2019/
STINGS: https://eitrawmaterials.eu/project/stings/
[21.06.2019] Publication: […] SAR IMAGES FOR MINING […].
EFTAS in ISPRS Geospatial Week 2019. … [read more]

04.06.2019EXPONOR 2019.
EFTAS with STINGS in Chile. read more04.06.2019EXPONOR 2019.
EFTAS with STINGS in Chile.
Around 1000 exhibitors and 40000 visitors attended the Exponor in Antofagasta, Chile, at the end of May.
Exponor is an international exhibition for the mining industry. It is a forum for the most important mining companies, suppliers and project specialists and offers a comprehensive overview of current market trends.
This year, one of the exhibitor areas served to present STINGS.
STINGS is a tailing monitoring service developed from an innovation project financed by EIT Raw Material, in which EFTAS is also involved. The monitoring service uses both remote sensing data and ground-based sensor information and thus offers a unique monitoring system for safety-relevant aspects such as stability and material delivery of tailing dams (see also: STINGS tailing monitoring.).
[04.06.2019] EXPONOR 2019.
EFTAS with STINGS in Chile. … [read more]

24.05.2019My name is LUCAS.
A product to our taste. read more24.05.2019My name is LUCAS.
A product to our taste.
LUCAS 2018 (LUCAS - a European wide mapping project.) is almost finished with this week's final meeting in Luxembourg.
Eurostat as client of this huge project and we as general coordinator for lot 3 and 4 are very pleased with the LUCAS product delivered.
We are also very pleased with a somewhat different LUCAS product. Because the LUCAS surveyor Javier Ibáñez Parra and Sergio Fernández Pedrón expressed their appreciation in a very special way. Javi and Sergio created a very own "My name is LUCAS" beer and sent us some bottles from the Spanish Ricote Valley. As soon as the last LUCAS points have been accepted, we will taste these bottles while looking back to the challenges we have mastered over the last months.
Javi and Sergio, thank you and the whole LUCAS team for the great work! It was a pleasure.
Kerstin, Dirk & Carsten
[24.05.2019] My name is LUCAS.
A product to our taste. … [read more]

15.03.2017Drones in good mission.
Micro Rapid Mapping with UAV. read more15.03.2017Drones in good mission.
Micro Rapid Mapping with UAV.
There are numerous useful applications for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV). Many of them in the remote sensing context. The reason is quite simple. An UAV is a platform with which local remote sensing data can be created quickly and flexibly. The data depend on the sensor, for example, aerial photographs or other spatially located measured values.
Rapid Mapping is established as fast emergency mapping in the environment of Emergency Management Services (EMS). It describes the fastest possible (geo-) supply of information to aid organizations after catastrophic events such as floods, earthquakes or forest fires. Well-known EMS are anchored in the European space program Copernicus. On the basis of satellite data of the affected region recorded as quickly as possible after the disaster, the damage situation can be recorded directly. How quickly the emergency mapping can be made available depends on when a suitable satellite is above the region and, in the case of optical systems, whether the cloud situation of the atmosphere permits images of the Earth's surface.
Following this rather large-scale approach, EFTAS has initiated Micro Rapid Mapping, a system for smaller-scale emergency mapping. The system is based on the automatic connection of current sensor data of a UAV with existing geodata in order to provide the fire brigade with optimal information immediately in highly dynamic local damage situations - for example a hazardous goods accident or a malfunction in the chemical industry.
The satellite sensor platform is therefore exchanged for the UAV in order to generate an extremely quickly available emergency map for smaller dangerous situations. The EFTAS system on board the UAV uses an RGB digital camera and a radiometric infrared camera. The data are transmitted immediately after recording to the ground via a powerful radio link and georeferenced ad hoc in a fully automated process, orthorectified and integrated as a layer into the system. The easy to use Micro Rapid Mapping system can be used autonomously by the emergency forces on site without the support of external GeoIT experts.
The project is funded by the Federal Ministry of Economics and Energy within the framework of the Central Innovation Management for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (ZIM) program. The project partner for the hardware and the development of the radio link is the company AiDrones GmbH.
[15.03.2017] Drones in good mission.
Micro Rapid Mapping with UAV. … [read more]

07.03.2019Warning via app.
Get alarm push messages. read more07.03.2019Warning via app.
Get alarm push messages.
The EFTAS city apps are available since a few years in Germany. Leisure and event tips, news and helpful information for everyday life for cities can be accessed via smartphone. From now on, the app can do even more: by connecting to the German Federal Emergency Information and Intelligence Service, the city app also provide information about dangerous situations. If, for example, a major fire breaks out or a hazardous substance spreads in the urban area, users will be immediately informed by a push message.
In addition the cities or emergency forces can also send their own warning messages. They can not only provide information about a hazard situation, but also ongoing information - for example if residents have to be evacuated. The messages appear immediately on the smartphone screen as push messages, i.e. the city app does not have to be opened for this.
App users will also be able to receive "normal" push messages. The city will provide details about upcoming events as well as important decisions and developments. "This type of combination of urban security messages and citizen information in one app is absolutely new," explains Dr. Andreas Müterthies, Head of Development at EFTAS. The reception of all messages is optional and can be switched on and off in the settings.
For the German city “Dülmen” the app for Android and iOS devices is available free of charge in the Google Play Store and in the App Store (under the title "Dülmen - Mein Revier”). The app is also linked to the municipal calendar of events and the Citizen Service of the city administration. Via a contact form, users can send questions and suggestions directly to the town hall and also attach photos or transmit their current location, e.g. if they have discovered a defective street lamp.
[07.03.2019] Warning via app.
Get alarm push messages. … [read more]

10.01.2019Visit from Sudan.
EFTAS organizes EO training for trainers. read more10.01.2019Visit from Sudan.
EFTAS organizes EO training for trainers.
Last December we had guests of the Remote Sensing and Seismology Authority from Sudan in Münster for a good week.
As part of the project "Climate Risk Finance for Sustainable and Climate Resilient Rain-fed Farming and Pastoral Systems" (CRFP), the "GIS AND EO TRAINING 2018" was on the agenda.
The aim of the training was to jointly train and execute the latest processing techniques of current and previous crop seasons monitoring and to provide the nominated experts with dedicated training for trainers on applied Earth Observation & GIS methods which are currently being implemented within the CRFP project in Sudan.
The successful training closed with a joint debriefing and discussion on the achieved results, possible improvements and next steps in view of an integration of the EO processing workflows into agricultural insurance framework.
See also:
CRFP -Workshop in Sudan.
[10.01.2019] Visit from Sudan.
EFTAS organizes EO training for trainers. … [read more]

04.12.2018Copernicus creates.
National Forum 2018 with EFTAS participation. read more04.12.2018Copernicus creates.
National Forum 2018 with EFTAS participation.
Last week three EFTAS employees were at the National Forum for Remote Sensing and Copernicus 2018 in Berlin. Even a glance at this year's "Copernicus creates" program showed that the operationalization of Copernicus is drawing ever larger circles. The spectrum of topics was correspondingly multifaceted and interesting.
EFTAS also participated in various event blocks. The EFTAS contributions were:
- Environmental and safety monitoring in mining regions with Copernicus, Dr. Andreas Müterthies
- Use of satellite image time series for grassland monitoring. Results of a national analysis for application to Natura2000 sites, Oliver Buck
- SenSituMon - Copernicus in analysis and monitoring of flood events, Dr. Bodo Bernsdorf
- Big Data approaches for predicting intra-urban heat islands, Dr. Bodo Bernsdorf and Dr.-Ing. Julian Bruns (GIScience Research Group, University of Heidelberg)
- DLM-Update (poster exhibition), Andreas Völker
This year, the program clarified how and where Copernicus data and services are used in Germany and how they shape our everyday lives. It was certainly not easy to represent the breadth of topics in one event. The organizers did a good job. We are excited to see whether the next events will remain cross-sectional or whether focus topics will be increasingly accentuated.
[04.12.2018] Copernicus creates.
National Forum 2018 with EFTAS participation. … [read more]

26.11.2018EFTAS on site in Romania and Chile.
STINGS consortium meets industrial partners. read more26.11.2018EFTAS on site in Romania and Chile.
STINGS consortium meets industrial partners.
STINGS is a development project to set up a monitoring system for tailing basins that uses remote sensing data in addition to terrestrial measurement data.
Test areas for the methodological work are located in Romania and Chile. Representatives of the consortium partners therefore met with actors from the local industrial partners - Romaltyn in Romania and Anglo American in Chile - in order to discuss the data situation and further joint action.
See also
STINGS tailing monitoring.
[26.11.2018] EFTAS on site in Romania and Chile.
STINGS consortium meets industrial partners. … [read more]

19.11.2018EFTAS on site in Namibia.
BIS consortium meets regional stakeholders. read more19.11.2018EFTAS on site in Namibia.
BIS consortium meets regional stakeholders.
For a good week, one BIS meeting followed another in Windhoek. The actors of the consortium and the local stakeholders got to know each other, expectations were put into concrete terms and technical possibilities were discussed.
At the end of the very intensive and constructive exchange everyone agreed: It will be challenging, but rewarding! The technical implementation now starts with a lot of team spirit.
See also
BIS in Namibia.
[19.11.2018] EFTAS on site in Namibia.
BIS consortium meets regional stakeholders. … [read more]

02.11.2018Flyer: From Münster to the world.
Worldwide customised GeoIT. read more02.11.2018Flyer: From Münster to the world.
Worldwide customised GeoIT.

12.10.2018European land monitoring conference.
EFTAS presented Natura 2000 mapping. read more12.10.2018European land monitoring conference.
EFTAS presented Natura 2000 mapping.
'European Land Monitoring at its crossroads – opportunities and challenges' was an international conference held in Innsbruck, Austria.
The purpose of the conference was to discuss the current state of the European public, scientific and industrial land monitoring capacities in face of increasing international competition.
EFTAS projectmanager Oliver Buck gave a talk on the subject of the Copernicus Natura 2000 Local Land Component service. EFTAS is coordinating the recent Natura 2000 mapping.
[12.10.2018] European land monitoring conference.
EFTAS presented Natura 2000 mapping. … [read more]

01.10.2018BIS in Namibia.
GIZ has commissioned EFTAS with a bush-WebGIS. read more01.10.2018BIS in Namibia.
GIZ has commissioned EFTAS with a bush-WebGIS.
Namibia's flying foxes would certainly like more baobabs in the savannah. They love the nectar of the tree blossoms. However, ecologists and sociologists are critical of the increasing proportion of woody plants in the savannah. Of course, the problem is not so much the number of baobabs, but above all the increasing bush cover. The grass-dominated ecosystem is an important livelihood for humans and animals. Farmers and their families make up about 70 percent of the Namibian population.
But the savannah is under increasing pressure due to the denser growth of bushes: the open pastures are overused, soil conditions deteriorate, in dry seasons the livestock do not always have enough fodder available.
New strategies for sustainable savannah management are already being researched. But the savannah ecosystem is very complex, especially with regard to the interactions between the geosphere and the biosphere. This can be seen, for example, in the close links between vegetation dynamics, soil moisture, groundwater, surface runoff and soil erosion.
EFTAS has now been commissioned by the German Society for International Cooperation (GIZ) to implement a Bush Information System for the continuous monitoring of Namibia's savannah. The project partners are Hansa Luftbild AG, the Council for Science and Industrial Research (South Africa), Namibia Ecosystem Services and Strydom & Associates Land surveyors (Namibia). By the end of next year, a WebGIS service will be developed to enable continuous satellite image-based monitoring and quantification of woody biomass.
In mid-November, an EFTAS team will set off for Windhoek to set the course for the successful project.
[01.10.2018] BIS in Namibia.
GIZ has commissioned EFTAS with a bush-WebGIS. … [read more]

24.08.2018NEXT project.
EFTAS works on new exploration technologies. read more24.08.2018NEXT project.
EFTAS works on new exploration technologies.
NEXT proposal has been compiled by a pan-European consortium, which consists of 16 partners leading coordinated by the GEOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS of Finland. The members come from 6 EU member states (Fi, FR, DE, MT, ES and SE) and represent the main metal producing regions.
NEXT will develop new geomodels, novel sensitive exploration technologies and data analysis methods which together are fast, cost-effective, environmentally safe and socially accepted. Methods developed reduce the current high exploration costs and enhance participation of civil society from the start of exploration, raising awareness and trust. Moreover, the reduced environmental impact of the new technologies and better knowledge about the factors influencing social licensing will help promote social acceptance of both exploration and mining and therefore support the further development of Europe´s extractive industry.
The first initial meetings of the work package participants have taken place and work on the individual work packages has started.
[24.08.2018] NEXT project.
EFTAS works on new exploration technologies. … [read more]

05.07.2018Publication: UAV use in chemical emergency situations.
Micro Rapid Mapping at GI_Forum in Salzburg. read more05.07.2018Publication: UAV use in chemical emergency situations.
Micro Rapid Mapping at GI_Forum in Salzburg.
“Micro Rapid Mapping: Automatic UAV-based Remote Sensing for Chemical Emergencies” is the title of the talk, Katharina Glock from German FZI Research Center for Information Technology gave at the GI_Forum 2018 (University Salzburg).
Now the Journal GI_Forum 2018 (Volume 1) provides the same named reviewed article. Co-authors are the EFTAS employees Dr. Bodo Bernsdorf und Sascha Woditsch.
Bibliographical reference:
GLOCK, K., MEYER, A. & BERNSDORF, B. & WODITSCH, S. (2018): Micro Rapid Mapping: Automatic UAV-based Remote Sensing for Chemical Emergencies.- in: GI_Forum 2018, Volume 1, Salzburg, p. 90 - 104
[05.07.2018] Publication: UAV use in chemical emergency situations.
Micro Rapid Mapping at GI_Forum in Salzburg. … [read more]

08.03.2018Freelance work offer.
EFTAS is looking for LUCAS surveyors. read more08.03.2018Freelance work offer.
EFTAS is looking for LUCAS surveyors.
For the mapping of LUCAS survey points in Denmark and the Netherlands we are looking for freelance surveyors for the mapping period May to August 2018.
Please find further inforation at Careers.
[08.03.2018] Freelance work offer.
EFTAS is looking for LUCAS surveyors. … [read more]

28.02.2018LUCAS - a European wide mapping project.
EFTAS was contracted for 2018 LUCAS Survey. read more28.02.2018LUCAS - a European wide mapping project.
EFTAS was contracted for 2018 LUCAS Survey.
By decision of the Statistical Office of the European Union (Eurostat), EFTAS was contracted to carry out the LUCAS Survey in 2018 in the countries of lots 3 and 4.
In addition to the regular collection of land cover and land use data, a new grassland module and a Copernicus component have been added to the on-site mapping.
Introductory information on LUCAS can be found here: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/de/web/lucas/overview
A study analyzing how LUCAS can contribute to the Copernicus land monitoring services can be found here: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/LUCAS_Copernicus_Report_v22.pdf
Further links:
[28.02.2018] LUCAS - a European wide mapping project.
EFTAS was contracted for 2018 LUCAS Survey. … [read more]

07.12.2017Flood? Then, there, so long!
SenSituMon - GeoIT for the analysis of flood events. read more07.12.2017Flood? Then, there, so long!
SenSituMon - GeoIT for the analysis of flood events.
Floods are natural events and cannot be completely prevented by structural flood protection. In the case of acute floods in inhabited areas, the key issues are: when does the flood occur, which areas are affected, how long will it last? The people affected naturally want to know, but so do the water management, agriculture and insurance industries. Tailor-made emergency management is the goal.
Level measurements and historical data are part of the classic approach to assessing flood events. Modern GeoIT offers the possibility of raising the level of information by merging classical data sources with analyses of satellite and in-situ sensor data. However, automated monitoring, implemented in an information service with which current analyses can be queried at any time, is still theory. The project SenSituMon focuses on the necessary technological developments for practical transfer.
EFTAS will work together with con terra and 52North on the development of (near) real-time information products for the automated large-scale monitoring of flood areas from satellite and in situ sensor data. An innovative focus is the topic "man as sensor". In the context of SenSituMon, it is rather "the human being as sensor carrier". Because it is about digital photos with position parameters, which are taken for example by rescue forces and spontaneous helpers working on site. The use of such photos is a promising approach for training the evaluation of satellite data with on-site information.
SenSituMon is used for status analysis. By archiving and feeding the data into evaluation models, a wide variety of forecasts are of course possible. Duration, damages or costs can be extrapolated. However, this will then be the task of the relevant user groups.
[07.12.2017] Flood? Then, there, so long!
SenSituMon - GeoIT for the analysis of flood events. … [read more]

02.11.2017WaCoDiS - New Copernicus service.
Water monitoring for dammed up lakes. read more02.11.2017WaCoDiS - New Copernicus service.
Water monitoring for dammed up lakes.
Climate changes and the ongoing intensification of agriculture effect in increased material inputs in watercourses and dams. Thus, water industry associations, suppliers and municipalities face new challenges. To ensure an efficient and environmentally friendly water supply for the future, adjustments on changing conditions are necessary. Hence, the research project WaCoDiS aims to geo-locate and quantify material outputs from agricultural areas and to optimize models for sediment and material inputs into watercourses and dams. Therefore, approaches for combining heterogeneous data sources, existing interoperable web based information systems and innovative domain oriented models will be explored.
Satellite remote sensing sensors of the European Copernicus program and data from the German Weather Service will be combined with an in situ sensor network for water monitoring. The aim is to increase the efficiency of environmental monitoring by means of innovative, automated methods for sensor data fusion and analysis. In particular, the focus is on water pollution control, water protection and securing access to clean drinking water.
For the first time a combined automated analysis of the Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data will be used to derive information on land cover as well as on the intra-annual variability of soil moisture and nutrient balance. In addition, data of the DWD will be included in order to analyze the effects of heavy rainfall events on the level of nutrient inputs.
After completion of the project, an innovative, web-based monitoring tool will be available, which has been comprehensively validated in various water management fields of action to prepare the operational use in test operations. The project partners thus provides water authorities, water management and wastewater associations as well as municipalities with an optimized toolbox of methods, applications and services for optimized environmental monitoring. The system will enable the localization of polluters and thus the timely development, implementation and monitoring of case-specific water protection measures. The project directly supports the implementation of the European Water Framework Directive and the Flood Risk Management Directive.
[02.11.2017] WaCoDiS - New Copernicus service.
Water monitoring for dammed up lakes. … [read more]

20.10.2017STINGS tailing monitoring.
New mining project for EFTAS. read more20.10.2017STINGS tailing monitoring.
New mining project for EFTAS.
In spite of its name, the STINGS project has nothing at all to do with a well-known British musician of the 1980s and 1990s. The acronym for the new mining project at EFTAS stands for “Supervision of Tailings by an Integrated Novel Approach to combine Ground-based and Space-borne Sensor Data”.
In mining, the term “tailings” refers to the fine-grained waste materials left over from the mining process. These materials are usually stored in large ponds constructed with impoundments, or in pits, both of which are intended to prevent the materials from leaching into the environment. The storage facilities are subject to regular monitoring and checks.
The STINGS project is developing a new approach that combines traditional measurement data with remote sensing data to further improve safety standards.
EFTAS is collaborating with six other partners on the project under the umbrella of the EIT RawMaterial research network.
[20.10.2017] STINGS tailing monitoring.
New mining project for EFTAS. … [read more]
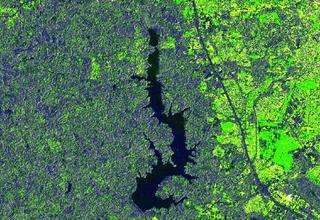
24.07.2017Press release: German-Brazilian cooperation: Mudak-WRM.
Reservoir drinking water quality – at a glance. read more24.07.2017Press release: German-Brazilian cooperation: Mudak-WRM.
Reservoir drinking water quality – at a glance.
New global methods set to simplify water protection / International research project headed up by Karlsruhe Institute of Technology / 2.6 million euros in funding from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research
In many parts of the world, reservoirs are used to store drinking water for citizens. But these reservoirs also collect sediments, fertilisers and hazardous substances which affect water quality. The German-Brazilian research project Mudak-WRM aims to develop a simplified model to predict reservoir water quality years in advance, and which can be deployed – at low cost – anywhere in the world.
The quality of water in reservoirs can vary significantly depending on the surrounding area from which it draws its contents. To depict reservoir processes accurately, the river basin that supplies the water must be incorporated into the model. If the reservoir is surrounded by intensively farmed or forested land, or by a densely populated area, large quantities of nutrients can enter the water course, resulting in over-fertilisation – or eutrophication – of the reservoir, which in turn encourages the growth of algae and, often, so-called “cyanobacteria”. If the water is subjected to long-term over-fertilisation, it is rendered unsuitable for use as drinking water.
A German-Brazilian research consortium led by KIT is working to develop a simple model that can be used to predict medium to long-term changes in water quality in reservoirs. The central goal of the research project, which was launched in April 2017, is to reduce the complexity of the underlying scientific approaches and data to enable the model to be deployed all over the world – including in developing countries – at low cost. “The lower level of complexity compared with existing models represents a major step towards the establishment of a transferable, globally functional model”, explains Dr Stephan Fuchs, head of the Mudak-WRM (multidisciplinary data acquisition as the key for a globally applicable water resource management) project. Fuchs leads the urban water management and water quality department at the KIT Institute for Water and River Basin Management.
The research project included studies of the Große Dhünntalsperre reservoir in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, and the Passauna reservoir in the Brazilian state of Paraná, along with the surrounding water sources. By comparing the results obtained from the two areas, the researchers can ensure that the findings are transferable to other reservoirs.
“We do not yet have a full understanding of the dynamic process that takes place between the water source and the reservoir itself, and this project will help us to close this gap”, says Hilgert. The project relies on innovative remote sensing technologies, including drones equipped with hyperspectral cameras, which use special sensor systems to detect very close wavelengths reflected off the body of water, supplementing the satellite images obtained by the European earth observation program Copernicus.
The German side of the project team, headed up by KIT – represented by its departments of water management and culture technology and urban water management and water quality, and the Institute of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing – also includes the University of Koblenz and Landau and industrial/public partner Wupperverband, as well as the companies 52°North – Initiative for Geospatial Open Source Software GmbH, EFTAS Fernerkundung Technologietransfer GmbH, Hydron GmbH and TRIOS Mess- und Datentechnik GmbH. On the Brazilian side, the project team comprises researchers from the Federal University of Paraná (UFPR) and the Universidade Positivo, as well as water supplier SANEPAR. Associated partners in Brazil include the Instituto Paranaense de assistência técnica e extensão rural (the Paranaensian institute for rural development, or EMATER) and the Instituto das Aguas do Paraná (the water board of the state of Paraná).
[24.07.2017] Press release: German-Brazilian cooperation: Mudak-WRM.
Reservoir drinking water quality – at a glance. … [read more]
04.07.2017Press release: EFTAS mapping for Copernicus N2K.
Extending the Copernicus Local Land Component. read more04.07.2017Press release: EFTAS mapping for Copernicus N2K.
Extending the Copernicus Local Land Component.
Current N2K mapping covers additional Natura 2000 sites.
Münster, 4.7.2017. The European Environment Agency (EEA) has commissioned a consortium made up of EFTAS, GAF and GeoVille to map additional grassland-rich Natura 2000 sites across Europe. This extends the coverage of the existing Copernicus Natura 2000 Local Land Component service. It is based on a visual interpretation of land cover and land use from very-high-resolution satellite imagery of the reference years 2006 and 2012. The first delivery unit containing around 22,000 km2 has been delivered to the EEA.
The Natura 2000 network of protected sites covers about 18% of the EU’s land area and is the main policy strategy to address biodiversity conservation in Europe. It is the world’s largest coordinated ecological network of protected areas, set up based on the legal requirements of the European Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive. Specifically, grassland habitats are an important component of biodiversity in Europe. Agricultural intensification and abandonment of traditional management practices have put these habitats under increasing pressure. Although protective legislation has been put in place, it has not yet been possible to stop the regional decline of important grassland habitat types.
The Natura 2000 (N2K) element is part of the Copernicus Land Monitoring Service Components and focuses on these hot spots of biodiversity and human activity. ‘To assure that Natura 2000 sites are effectively preserved, harmonized information on land cover change dynamics and periodic monitoring across Europe is inescapable’, explains Oliver Buck, project manager of EFTAS and responsible for the overall production and quality assurance, with respect to the main N2K benefits. The N2K service element provides comparable, pan-European and very-high-resolution (VHR) information on land cover and land use (LC/LU) status and changes over time for selected grassland-rich Natura 2000 sites across Europe, including a 2 km buffer zone around each protected site. The service differentiates 55 thematic LC/LU classes specified according to the MAES framework (Mapping and Assessment of Ecosystems and Their Services). All information is based on satellite image classification for the reference periods 2006 and 2012. The change mapping layer makes use of the LC/LU 2012 status information, applying a visual change interpretation using the VHR satellite imagery. It provides quantitative and qualitative information on land cover change dynamics between 2006 and 2012. The resulting LC/LU information will be used to support biodiversity conservation in Europe, such as analyses on pressures and threats within Natura 2000 sites and in their surroundings.
The current survey is intended to complement and continue the previous mapping under the Copernicus Initial Operation phase (GIO) to a maximum area of around 470,000 km² until mid-2019. So far, EFTAS, GeoVille and GAF (together with its subcontractor Telepsazio Iberica) have provided the first 22,000 km2 according to schedule.
Source cover picture:
https://na.unep.net/atlas/africaWater/images/maps/pngs/annual_average_rainfall.png
Source text picture:
http://www.eftas.de/upload/11790878-GMFS3-Promotion-Brochure.pdf
[04.07.2017] Press release: EFTAS mapping for Copernicus N2K.
Extending the Copernicus Local Land Component. … [read more]

14.06.2017Right?
Validating geodata based on remote sensing. read more14.06.2017Right?
Validating geodata based on remote sensing.
Satellite and aerial image data are used to observe and analyse the earth. Thematic land cover maps are created with the image data and serve as the basis for knowledge and decisions in politics, business and administration.
This begs a not insignificant question: How reliable is this geodata?
Naturally, this varies from dataset to dataset depending on the specifications and how it was produced. Therefore, datasets based on remote sensing are validated before release. Inconvenient and extremely complex, this step is not exactly popular. However, validation is necessary if qualitative standards are to be fulfilled and documented reliably; statistical procedures determine values indicating the quality of a dataset. In light of growing data stocks and increasingly automated analysis, it is ever more important to have standardised validation procedures with results that can be reproduced and compared. While statistical theory offers the most complex methods, operational practice requires robust instruments. And therein lies the stumbling block between theory and practice*. This has been confirmed by the SIGMA project network. SIGMA (Stimulating Innovation for Global Monitoring of Agriculture) is an international network of experts who work together to consolidate operational remote sensing methods. It is aided by ten JECAM (Joint Experiment of Crop Assessment and Monitoring) test sites spread across four continents.
EFTAS has developed a standardised concept for validating remote sensing-based geodata within the SIGMA network and offered it up for discussion. Building on this, GeoIT plug-ins have been developed that support individual validation steps based on open sources and free libraries. The JRC (Joint Research Centre) and FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) were also involved. This has resulted in validation guidelines that are well founded yet easy to understand and linked with simple yet practical implementation tools. Practical relevance means that these tools and guidelines are used with increasing frequency, often when planning remote sensing projects.
Further links:
Guideline: SIGMA - validation protocol.
*see also
Foody, G.M. (2002) ‘Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment’. Remote sensing of environment 80, 185–201.
Olofsson, P., Foody, G.M., Stehman, S.V., Woodcock, C.E. (2013) ‘Making better use of accuracy data in land change studies: Estimating accuracy and area and quantifying uncertainty using stratified estimation’. Remote Sensing of Environment 129, 122–131. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2012.10.031
[14.06.2017] Right?
Validating geodata based on remote sensing. … [read more]

09.06.2017Guideline: SIGMA - validation protocol.
Protocol for land cover validation. read more09.06.2017Guideline: SIGMA - validation protocol.
Protocol for land cover validation.

25.05.2017!شكرا جزيلا
CRFP -Workshop in Sudan. read more25.05.2017!شكرا جزيلا
CRFP -Workshop in Sudan.
The “CRFP Geo Data technical workshop” took place last week in the National Center for Research in Khartoum. Geoinformation is the crucial basis for the “Climate Risk Finance for Sustainable and Climate Resilient Rain-Fed Farming and Pastoral Systems” project (see also When the rain doesn’t come). However, many of the people involved in the project are not GeoIT experts. Our role was therefore to establish a common understanding of the uses and benefits of GeoIT and remote sensing data. Together with Dr Solafa Babiker Mohammed from the Sudanese RSSA (Remote Sensing and Seismology Authority), we presented the relevant geo datasets and their potential uses. This information enabled the workshop attendees to reflect on and discuss the further project steps proposed.
We believe that a good common understanding has now been reached within the project of the uses and benefits of GeoIT, along with a promising action plan supported by all.
Carsten Haub & Luca Kleinewillinghöfer
[25.05.2017] !شكرا جزيلا
CRFP -Workshop in Sudan. … [read more]
18.04.2017When the rain doesn’t come.
Credit and insurance management in Sudan with GeoIT. read more18.04.2017When the rain doesn’t come.
Credit and insurance management in Sudan with GeoIT.
Over the last few days, there have been reports that April is too dry and too cold. While this might not be great for farmers, it won’t necessarily threaten their livelihoods. Not so in Sudan, where the coming weeks will determine this year’s crop yields. The rainy season begins in mid-June, and if it goes badly, there will be no crops. Extreme fluctuations in annual rainfall are characteristic of this region between the Sahara and tree savannah, and they are becoming even more extreme as the climate changes. For smallholder rain-fed farmers and pastoralists, this is a fight for survival.
Up to now, there have been no sustainable credit and insurance instruments to minimise the financial risk for these farmers. But this is set to change, as the Sudanese government engages in a large-scale, cross-ministry project. The foundations are being laid in an initiative from the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) entitled “Climate Risk Finance for Sustainable and Climate Resilient Rain-Fed Farming and Pastoral Systems in Sudan” (CRFP Sudan).
A GeoIT system is being set up and satellite data is being incorporated to monitor the climate and to record and assess agricultural areas. This will provide the state and banking or insurance companies with sophisticated geodata to develop and apply suitable credit as well as insurance products for the Sudanese farmers affected. The project is being led by the Sudanese Remote Sensing and Seismology Authority (RSSA).
EFTAS is supporting the project with its long-standing expertise in remote sensing in Africa and its experience in on-site collaboration with national bodies. EFTAS focuses on implementing adapted procedures for processing satellite data, providing GeoIT applications for agricultural monitoring, systematically incorporating supplementary field mapping, ensuring quality standards and training in-country experts.
Source cover picture:
https://na.unep.net/atlas/africaWater/images/maps/pngs/annual_average_rainfall.png
Source text picture:
http://www.eftas.de/upload/11790878-GMFS3-Promotion-Brochure.pdf
[18.04.2017] When the rain doesn’t come.
Credit and insurance management in Sudan with GeoIT. … [read more]

30.01.2017Raw materials sector needs Geo-IT.
EFTAS new EIT RawMaterials partner. read more30.01.2017Raw materials sector needs Geo-IT.
EFTAS new EIT RawMaterials partner.
The European Institute of Innovation and Technology (EIT) brings together cutting-edge research into ways to improve Europe's ability to compete. The EIT acts as an umbrella organisation and promotes innovation communities from the knowledge triangle of education, research and industry (Knowledge and Innovation Communities – KICs) covering areas such as climate change, renewable energies and information and communication technology.
EFTAS has also been a member of the EIT RawMaterials KIC, formed in 2014, since the end of 2016.
EIT RawMaterials is Europe's largest and most significant research network in the field of raw materials. It combines excellence and market potential. More than 100 partners from the worlds of business and academia, from a total of 22 EU member states, have joined forces to incorporate innovations stemming from research into the European raw materials industrial sector.
The use of digital resources is becoming ever more important in ensuring secure access to raw materials, sustainable resource management and resource efficiency.
That is why EFTAS is contributing its geo IT expertise to the EIT RawMaterials network in order to promote sustainable exploration, extraction, recycling and substitution of raw materials by analysing geoinformation.
See also:
[30.01.2017] Raw materials sector needs Geo-IT.
EFTAS new EIT RawMaterials partner. … [read more]

18.01.2017Copernicus@work in Berlin.
EFTAS at Copernicus Forum 2017. read more18.01.2017Copernicus@work in Berlin.
EFTAS at Copernicus Forum 2017.
Whenever the German Aerospace Center and German government organise the German National Forum for Remote Sensing and Copernicus, EFTAS is invariably there.
This series of events targets traditional potential Copernicus users in order to communicate the potential uses of Copernicus as a valuable digital information base with regard to efficient public administration, innovative private-sector services and science.
That is also an important concern for EFTAS. That is why we will once again be exhibiting our latest developments at the sixth instalment of the forum, held at the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure (BMVI) in Berlin from 14 to 16 March 2017.
These are EFTAS contributions on the programme:
- Keynote: Copernicus im Feuerwehr-Einsatz, Dr. Bodo Bernsdorf
- Session A.1: Satellitengestützte Fernerkundung zur Stärkung von Subsistenzlandwirtschaft und Transhumanz im Hinblick auf klimatische Schwankungen im Sudan, Alexandra Biscan
- Session A.3: GMES4Mining - Copernicus-basierte Dienste für den Bergbau, Dr. Kian Pakzad
- Session D.1: Bedeutung und Auswirkungen der erneuerbaren Energien auf Natura2000 Gebiete, Oliver Buck
[18.01.2017] Copernicus@work in Berlin.
EFTAS at Copernicus Forum 2017. … [read more]
11.01.2017More Copernicus Local Land Component data.
EEA contract for Natura 2000 mapping. read more11.01.2017More Copernicus Local Land Component data.
EEA contract for Natura 2000 mapping.
The Europe-wide network of Natura2000 conservation areas is at the heart of European policy on long-term nature conservation and the preservation of biodiversity. The European Environment Agency (EEA) has now commissioned a consortium of companies comprising EFTAS, GAF and Geoville to use satellite imagery to record the condition and rate of change of a selection of Natura2000 regions consisting mainly of grassland covering a large surface area.
This builds on the local component of the European Copernicus programme aimed at providing pan-European data for specific issues.
EFTAS is coordinating the consortium and will undertake approximately 190,000 km2 of the mapping, representing the largest share of the project. In this context, 55 land cover and land use classes will be recorded for the 2012 and 2006 time windows over the next 30 months.
[11.01.2017] More Copernicus Local Land Component data.
EEA contract for Natura 2000 mapping. … [read more]

05.01.2017Geoinformation for landscape planning.
Three new contracts for biotope type mapping. read more05.01.2017Geoinformation for landscape planning.
Three new contracts for biotope type mapping.
Led by ARGE Kortemeier Brokmann Landschaftsarchitekten, the foundations are due to be laid in spring 2017 for updating the landscape structure plans for the Osnabrück and Schaumburg districts and the landscape plan for the Herford district.
In order to update the content of these plans, the biotope types present must be recorded again in each case. So as to limit the time and effort needed to undertake full terrain recordings, recordings based on aerial images will be collected beforehand and combined with local mapping.
EFTAS has been commissioned to collect these aerial-image-based biotope type recordings.
[05.01.2017] Geoinformation for landscape planning.
Three new contracts for biotope type mapping. … [read more]

21.11.2016EFTAS at d-copernicus.de!
DLR documents EFTAS Copernicus expertise. read more21.11.2016EFTAS at d-copernicus.de!
DLR documents EFTAS Copernicus expertise.
Within the frame of D-Copernicus Web Portal the German Aerospace Center (DLR) offers a database that contains qualified remote sensing companies and institutes based in Germany.
The EFTAS record presents many examples of Copernicus relevant EFTAS activities.
Graphic source: www.d-copernicus.de
[21.11.2016] EFTAS at d-copernicus.de!
DLR documents EFTAS Copernicus expertise. … [read more]

01.11.2016GeoIT for mining technology.
Research center Nachbergbau cooperates with EFTAS. read more01.11.2016GeoIT for mining technology.
Research center Nachbergbau cooperates with EFTAS.
From space the ‘Ruhrgebiet’ is a real eye-catcher: at night millions of lights twinkle and during the day it looks much greener than expected. But satellites also show where mining has had its impact. The research center Nachbergbau of the Technical University Georg Agricola uses the satellite imagery to develop innovative monitoring methods for former mines and redeveloped areas. Also an early warning system for the consequences is possible in the long-run. That’s why the researchers now work together with EFTAS GmbH in Münster.
“EFTAS provides the experts for interpretation of areal and satellite imagery – we from the research center Nachbergbau are the experts on the ground and we have access to information on redevelopment from terrestrial sources” says Prof. Dr. Peter Goerke-Mallet. This information includes mining specific maps but also on site measurements and surveys.
Together we can develop tailor-made solutions for the many aspects of mine-redevelopment.
“The structures of mining have for instance an impact on hydraulics. Some of the hydraulic changes can be recorded with satellite sensors and so the first signs of an impact on the surface are detected. This helps to detect spatial – temporal processes and to detect dangers“ explains Prof. Dr. Christian Melchers, scientific head of the research center Nachbergbau. The experts of Nachbergbau also want to develop an early warning system with the geo-data of EFTAS.
Possible ground movements are also examined: “especially effective are these measurements for build-up areas without vegetation. This means we have a lot of potential here in the Ruhrgebiet””, says prof. Melchers.
To monitor complete regions for environmental purposes, we have to process enormous amounts of data, explains Dr. Andreas Müterthies von EFTAS. “Data mining is the IT-approach that will be used to combine the mining data with the satellite remote sensing data. For the first time these remote sensing data are available through the European ‘Copernicus’ program for the whole area. New possibilities for the continuous monitoring of changes in former mining areas arise”.
[01.11.2016] GeoIT for mining technology.
Research center Nachbergbau cooperates with EFTAS. … [read more]

10.10.2016Flyer: DLM-Update.
Change Detection as easy as it seems. read more10.10.2016Flyer: DLM-Update.
Change Detection as easy as it seems.
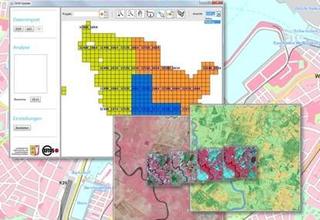
07.10.2016DLM-Update meets 3A-products.
EFTAS and AED-SICAD sign cooperation agreement. read more07.10.2016DLM-Update meets 3A-products.
EFTAS and AED-SICAD sign cooperation agreement.
The use of remote sensing to update vector data sets.
EFTAS Fernerkundung Technologietransfer GmbH (EFTAS), Münster, and AED-SICAD AG, Bonn, have signed a cooperation agreement. The goal of the cooperation is to provide an integrated solution for the use of remote sensing to update existing vector data.
The basis of the product will be formed by the Land management product line, the 3A products of the AED-SICAD as well as the DLM-Update of EFTAS and the “Landesamtes für Vermessung und Geoinformation” in Schleswig-Holstein. “ We have found that our products, skills and services are complementary to a large extend. Our 3A product family focuses among others on the management of basic geo data of the land registry and the survey department. Moreover we have plenty of experience with the update of these data using our 3A-model”, says Markus Müller, manager Public Sector of AED-SICAD. EFTAS on the other hand has many years of experience with the use of satellite data and areal imagery.
Both companies respond to the increasing demand for useful methods for the update of vector data sets using information from remote sensing. Especially important is that this application makes it possible to have current vector data.
“Satellite remote sensing data is getting more and more precise and less expensive at the same time. When we connect our products we contribute to the update of data sets by using remote sensing data”, emphasizes Dr. Andreas Müterthies of the R&D section of EFTAS.
[07.10.2016] DLM-Update meets 3A-products.
EFTAS and AED-SICAD sign cooperation agreement. … [read more]

05.09.2016Folder: Geoinformation and IT Services
EFTAS.GeoIT read more05.09.2016Folder: Geoinformation and IT Services
EFTAS.GeoIT
29.08.2016Latest news about „DLM-update“.
EFTAS will give a speech at GEOBIA 2016. read more29.08.2016Latest news about „DLM-update“.
EFTAS will give a speech at GEOBIA 2016.
At this year’s GEOBIA (Enschede, 14.-16.9.2016) Andreas Völker will present the actual state of affairs concerning the automated update of the ATKIS©-Basis-DLM through remote sensing:
DLM-Update - Integration of earth observation technologies in IT structures of the national mapping authorities in an use case: Update of the ATKIS®-DLM of the State Bureau of Surveying and Geoinformation Schleswig-Holstein.
GEOBIA - GEOgraphic-Object-Based Image Analysis - is an evolving sub-discipline of GIScience devoted to partitioning remote sensing (RS) imagery into meaningful image-objects, and assessing their characteristics through spatial, spectral and temporal scale.
During the last 10 years the GEOBIA community has grown from a niche discipline to a recognized and vibrant branch of geoinformation science, and methods developed by the growing community have helped to tackle problems in virtually all domains where geographic data are used.
The decennial GEOBIS-conference-anniversary will take place at the Faculty of Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation (ITC) of the University of Twente, in Enschede, The Netherlands, from 14-16 September 2016.
Link conference homepage.
[29.08.2016] Latest news about „DLM-update“.
EFTAS will give a speech at GEOBIA 2016. … [read more]

23.08.2016Red-hot at EFTAS.
GeoIT-Offers for Fire Services. read more23.08.2016Red-hot at EFTAS.
GeoIT-Offers for Fire Services.
How do officers-in-charge get fast decision support using spatial data? Which spatial base data are available and how to use them legally compliant and technically rational on incident sites?
Our new products and services give an answer. The modular offers consist of Software, Consulting, Data-Services/-Production and Development.
Our offers are generated by firemen to be used by firemen and are affordable for even small fire brigade – guaranteed.
See also:
[23.08.2016] Red-hot at EFTAS.
GeoIT-Offers for Fire Services. … [read more]

15.07.2016It is there!
The new EFTAS web site is on line. read more15.07.2016It is there!
The new EFTAS web site is on line.
Welcome to the new EFTAS web site.
Together with the WN Online Service from the ‚Aschendorff Unternehmensgruppe‘ EFTAS has developed a new web site concept. Modern design, current content and modern techniques are the ingredients.
Main feature: you can learn about us and our Geo IT Solutions as well from the technology perspective as from the projects. Main short project presentations connect the basic descriptions of technologies with practical examples and invite you to nose around.
If you already have some key words, you can select relevant technologies and projects from the EFTAS content pool.
We hope our new concept works. Your feedback and comment is welcome.
[15.07.2016] It is there!
The new EFTAS web site is on line. … [read more]

05.07.2016We use the gate to the world.
EFTAS is exhibitor at the Intergeo 2016 in Hamburg. read more05.07.2016We use the gate to the world.
EFTAS is exhibitor at the Intergeo 2016 in Hamburg.
As a loyal Intergeo exhibitor EFTAS will be present in Hamburg from the 11th – 13th of October.
Our motto for this year’s fair for Geodesy, Geo information and Land management: The world changes. We will see! The demands of the modern world also reflect on geo information.
Solutions for maintenance of official Geo data in 3D with photogrammetry and the mapping of change detection for land cover and land use with (Sentinel) satellite data are our main themes this year.
For the land register, nature conservation, environment or for tourist information, our solutions work for official building registers, updates of biotope maps or for apps for tourists. Precise and Efficient.
Our booth: E4.002 (Hall 4).
[05.07.2016] We use the gate to the world.
EFTAS is exhibitor at the Intergeo 2016 in Hamburg. … [read more]

15.02.2016For planted housetops.
EFTAS is working together with Green roof associations. read more15.02.2016For planted housetops.
EFTAS is working together with Green roof associations.
The International Green Roof Association (IGRA), the Deutsche Dachgärtner Verband e.V. and EFTAS Fernerkundung Technologietransfer GmbH have signed an agreement. EFTAS will act as technology partner for the mapping of green roofs and the green roof potential.
[15.02.2016] For planted housetops.
EFTAS is working together with Green roof associations. … [read more]

01.02.2016Experience nature.
New app „Erlebnis Naturerbe“. read more01.02.2016Experience nature.
New app „Erlebnis Naturerbe“.
With the app Erlebnis Naturerbe you can compose your own tours through the nature reserves and scenery of Westfalen. Experience the natural heritage walking or cycling. Available for Android, iOS and Windows Phone.
More information: erlebnis-naturerbe.de
Windows Store:
https://www.microsoft.com/store/apps/9NBLGGH1M8TW
[01.02.2016] Experience nature.
New app „Erlebnis Naturerbe“. … [read more]

01.02.2016Striking changes.
ArcGIS-Tool and Sentinel data for the analysis of FFH habitat types. read more01.02.2016Striking changes.
ArcGIS-Tool and Sentinel data for the analysis of FFH habitat types.
The Habitats Directive (FFH-RL in Germany) forms the central legal basis for nature conservation in the European Union (EU). FFH (Fauna-Flora-Habitat) areas are part of the Natura 2000 network of protected areas and are subject to monitoring and reporting requirements.
Conservation status and future outlook of the FFH-habitat types (LRT) have to be assessed on a regular basis. The Directive was passed more than 20 years ago. Currently, the basis for the specified monitoring method are field surveys.
The EFTAS solution FELM (i.e. “Fernerkundungsgestützte Erfassung von Lebensraumtypen für das FFH-Monitoring”) minimises the amount of field surveys and increases the efficiency of the monitoring.
FFH monitoring at its core means earth observation. A variety of satellite systems is observing the earth with their sensors. On the basis of these satellite images the earth surface can be classified into different land cover classes and geometrically delineated.
Modern methods of remote sensing allow a further automatization and refinement of these geometric delineations and class definitions. The challenge grows with the number of classes that have to be differentiated. The FFH-RL distinguishes between 231 habitat types. However, the remote sensing based identification of these habitat types is a challenge.
The FELM software checks whether there are any change notices due in the LRT field surveys of the FFH area to be monitored. LRT objects that have changed can then be further analysed. These change notices result from the analysis of a time series of satellite images. The distribution of satellite images throughout the year allows the collection of additional data on vitality and phenology of vegetation as well as on indicators such as surface structure and land use (e.g. mowing of pasture) that help with the LRT identification. Objects with signs of change are filtered out by comparing all indicators with LRT typical patterns.
FELM is a pilot development for the state of North-Rhine Westphalia and is integrated into the existing GeoIT infrastructure as an ArcGIS extension. The system has become economically viable because cost free Sentinel satellite data from the European Copernicus programme could be used.
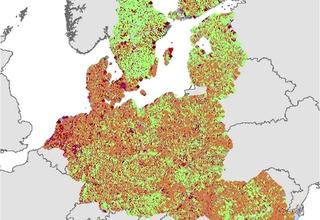
01.02.2016Point by point detection.
LUCAS – a European wide mapping project. read more01.02.2016Point by point detection.
LUCAS – a European wide mapping project.
Imagine covering the whole of Europe with a sampling grid of 2 x 2 km generating 270.000 intersection points that are used to map land use and land cover on the ground. No matter, whether it is agriculture, forest or urban area.
A mammoth task? Of course. But absolutely essential for EUROSTAT. For years, EFTAS has been substantially involved in the accomplishment of this task, together with a strong partner network. EUROSTAT is the statistical office of the European Union and responsible for the provision of statistics at European level. LUCAS (Land Use/Cover Statistical Area Frame Survey) provides fundamental and harmonised information
on land use and land cover that can be used for long term observations, e.g. sealing, soil degradation, the impact of agriculture on the environment and the degree of landscape fragmentation. LUCAS is a stratified sample on the basis of a regular point grid covering the whole of the EU’s territory. It has become an operational EUROSTAT standard to provide harmonised, geostatistical information. The first LUCAS survey was held in 2001. Since 2009, the LUCAS survey is carried out operational in a three-yearly interval.
Until now, EFTAS has always been involved in carrying out the survey. In 2015, EFTAS was responsible for the collection of survey points in Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Finland and the overall coordination of point collection in 10 other member states.
The mapping requirements have continued to develop since 2001. The set of rules is by no means trivial. Land cover is differentiated into 69 classes, land use into 33 classes. Starting from the survey point, these classes are recorded on a 250 m transect in eastward direction. Moreover, pictures are taken at the point in all four cardinal directions. On the ground, the surveyor also collects information on a further 60 parameters in order to provide a differentiated description of the survey point. A top soil sample is taken for 10 % sample of the surveyed points.
Just like the survey methodology, the management of the project is very complex. EFTAS has been coordinating a European wide network of surveyors and partner companies. The implementation of the survey requires extensive preparation. To ensure the efficient running of the project, the surveyors are professionally trained and technically equipped by EFTAS. To support the surveyors in the field, EFTAS has developed an App called PLOP. Nevertheless, the back office remains the main central authority for the direct clarification of urgent questions from the surveyors in the field. With the beginning of the field survey, the internal quality control as well as the processing of data for delivery to the external quality control by EUROSTAT plays a vital role. EFTAS is judged by its continuous high quality of data.
Besides the provision of statistical data for socio-environmental studies, LUCAS has become of further significance in the context of COPERNICUS. COPERNICUS, previously known as GMES (Global Monitoring for Environment and Security), is the European Programme for the establishment of an autonomous European satellite infrastructure including Earth Observation services. The terrestrial survey data of LUCAS serve as a valuable addition to the COPERNICUS services. Details on how to integrate the data have been documented in a recent study conducted by a European expert network.

19.01.2016App to explore the river Wupper.
Modern nature tourism in the region Bergisches Land. read more19.01.2016App to explore the river Wupper.
Modern nature tourism in the region Bergisches Land.
The initiative „WupperVielfalt“ has a praiseworthy objection with regard to the region Bergisches Land. It intends to display the connection between historic elements of the industrial landscape and valuable natural areas.
EFTAS developed an App with theme routes.
The river Wupper is the connecting element in the region. In the most recent past, this has not always been the case. Not too long ago the Wupper looked more like a grey-brown band as a result of industrialisation. Meanwhile, some of the natural spaces that can be found among the old industrial and cultural areas have Europe-wide significance. Besides offering an interesting natural landscape, the touristic infrastructure is well developed and offers a variety of hiking and bike trails to explore the area. These are ideal conditions to disseminate this knowledge on natural spaces and the necessity for their protection.
In this context, the Biological Station Oberberg has realised adventure stations. Along the Wupper between Marienheide, Wipperfürth, Hückeswagen and Radevormwald, 26 adventure stations have been installed displaying information on fauna, flora, habitats and characteristics of this cultural landscape.
Together with the „Bahntrassenradweg“ (a cycle path on an abandoned railway track), the bird observation station in Wipperfürth-Leiersmühle, the „Auenpark“ in Hückeswagen and the „Basisstation Wasserquintett“ (information centre), these adventure stations form the backbone of the nature-based tourism infrastructure as well as the basis of information for the App with theme routes developed by EFTAS. Via smartphone cyclists, hikers and walkers can choose their individual route as well as download additional information on other points of interest.
Google play:
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.eftas.wuppervielfalt.app
Homepage and image source: Biologische Station Oberberg:
http://www.biostationoberberg.de/wuppervielfalt.html

07.01.201630 ha per day is enough!
Evaluation of different data sources for the monitoring of land consumption. read more07.01.201630 ha per day is enough!
Evaluation of different data sources for the monitoring of land consumption.
A lot of building activity is taking place in Germany. Industrial estates, shopping centres, residential areas, roads. The plan of the National Sustainability Strategy outlines that by 2020 less than 30 ha per year of “green area” should be overbuilt with residential and traffic areas.
How can this goal of 30 ha be realised? Which data base provides the ideal reference? There are large differences in official data sets. The following publication by Spiegel online on the 11.11.2014: "Germany is growing by the size of Liechtenstein" referred to area data of the Federal Statistical Office. At the end of 2013, the ground area of Germany was approximately 17.000 ha larger than in the year before. The reason for this was a change in the state of Brandenburg from the previous basis for calculation, the ALB (“Automatisiertes Liegenschaftsbuch”) to the geometry based ALKIS (“Amtliches Liegenschaftskatasterinformationssystem”).
In future, real estate book and map will be integrated into one unit, therefore their values will have to be aligned.
On behalf of the Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety as well as the Federal Institute for Research on Building, Urban Affairs and Spatial Development, EFTAS analysed the land statistics for possible inaccuracies. Other potential application possibilities of additional data sources such as the Digital Landscape Model (ATKIS-Basis-DLM) were also investigated.
The results in short:
- The ALKIS-Migration worked well with regard to the land area categories
- In terms of change from book area to geometry-based area case studies showed inaccuracies of 0,4 % with regard to the daily land usage
- Currently, there are no alternative remote sensing based data sources that could completely replace ALKIS in terms of accuracy and area coverage.
In conclusion it can be said that following the ALB – ALKIS migration and the complete update of the „real land use“, a single instrument is now available nationwide as a basis for land area monitoring.
Source of figure: „BERNSDORF, B. (2015): Evaluation der Datenbasis für die Flächennutzungsstatistik.- in: Meinel, G., Schumacher, U., Behnisch, M. & Krüger, T. [Hrsg.] (2015): Flächennutzungsmonitoring VII: Boden – Flächenmanagement – Analysen und Szenarien, IÖR-Schriften, Band 67, Berlin, S. 29 – 38.“
04.01.2016Next Generation.
GIS in times of big data. read more04.01.2016Next Generation.
GIS in times of big data.
Humankind is producing enormous amounts of digital data. Meanwhile, this fact has become common knowledge. The same holds true for data base approaches and management tools for the organisation of data streams that are becoming increasingly faster and more diverse.
The new approach of the future is to realise that we do not need all the data. Promising are the new concepts that tell us what we really need: which patterns generate new findings and have to be examined more closely in order to support quick and better decisions on the basis of this “dimensionally reduced” heterogeneous data.
BigGIS helps to research and develop a new generation of geographic information systems. These will be predictive and prescriptive geographic information systems, based on high-dimensional geo-temporal data structures. Available data can basically be looked at as features in terms of space and time.
The challenge lies in the integrated analysis of spatial and temporal geodata with additional heterogeneous and incomplete data. Data which does not fulfil the requirements in terms of area coverage or resolution from our understanding of quality. Data from a variety of sources such as remote sensing, crowdsourcing, social web and legacy systems for the processing of geodata.
Prototypical solutions are developed and validated for application areas such as „hazard prevention“, „environment“, as well as „smart city and health“.

01.01.2016Sustainable and constant supply of rubber.
Remote sensing for the detection of rubber plantations along the Mekong river. read more01.01.2016Sustainable and constant supply of rubber.
Remote sensing for the detection of rubber plantations along the Mekong river.
Latex is the sap of the tropical rubber tree Hevea brasiliensis and contains caoutchouc. The rubber tree can be seen as a guest in the southern tropical regions of China and the neighbouring countries of the Mekong region.
Traditionally, the tree originates from South America. However, the use of this tree also causes problems. One of the reasons is the world economy and its growing demand for natural rubber as a result of the economic boom in Asia. For many small farmers, the cultivation of rubber trees in monocultures is the only way to escape poverty.
As a result, rubber tree plantations in the Mekong region are expanding at the expense of natural forests belonging to the “Indo-Burma hotspot“, one of the world’s richest biodiversity regions. The overall objective of the joint project SURUMER is the development of an integrative land management concept for sustainable rubber cultivation in the Chinese province of Yunnan. SURUMER is the acronym for “Sustainable Rubber Cultivation in the Mekong Region”.
The project investigates the impact of the rubber boom on the environment and living conditions of the population as well as possibilities to minimise negative impacts. To be able to transfer the selective results to larger areas the size and location of plantations must be known.
Within SURUMER, EFTAS is responsible for the provision of information obtained from remotely sensed data.
On the basis of field-based reference data, the so-called „ground truth“, the classification system is trained to distinguish typical statistical characteristics of different land use and land cover.
With the help of this sample data a supervised classification can be performed where colour values and textures in the satellite imagery as well as elevation data is used to classify the actual land cover in the project area.
Although the remote sensing methodology developed in SURUMER can be seen as a prototype, the resulting concept can be transferred to other areas in the Mekong region. Ideally, the processes should be adjustable to other extensive tropical monocultures.

01.01.2016LUCAS and Copernicus.
Synergies of European geospatial data sets. read more01.01.2016LUCAS and Copernicus.
Synergies of European geospatial data sets.
LUCAS and Copernicus. Two variables in the European geodata scene. They both describe programs for the provision of pan-European land use and land cover information. Each program has its own history, its own intention and its own justification. The Land Use/Cover Area Frame Survey, in short LUCAS [Link intern nn], is a European-wide survey that provides comparable statistics on land use and land cover on the basis of a systematic area sampling. The surveyed points are analysed statistically by the European commission.
The goal of Copernicus, previously known as GMES (Global Monitoring for Environment and Security), is the establishment of a European infrastructure for environmental monitoring. Copernicus has a fleet of earth observation satellites to produce specific geoinformation services.
Therefore, LUCAS and Copernicus are two completely different programs. On behalf of the European Topic Centre Urban, Land and Soil (ETC/ULS) and the European Environmental Agency (EEA), EFTAS analysed the interfaces of these two programs with regard to the aspect of monitoring. How do these two programs fit together with regard to temporal, thematic and spatial processes as well as data models?
The study proved that LUCAS can make a contribution to the Copernicus program. On the basis of the results, recommendations were made for the improvement and harmonisation of different data models and processes. Not only were further empirical analyses proposed, but it was also initiated to provide results to the EAGLE working group (Eionet [European Environment Information and Observation Network] Action Group on Land monitoring in Europe). This group advocates the harmonisation of geoinformation on land cover on a European level.
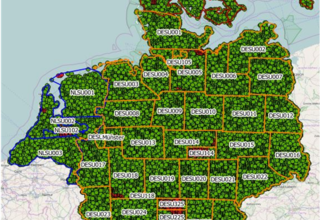
01.01.2016Working in the field.
App for the real-time-management of field surveys. read more01.01.2016Working in the field.
App for the real-time-management of field surveys.
The App PLOP was developed by EFTAS to facilitate the execution of complex and large scale mapping projects. PLOP stands for „Progress logging for Land Observation Projects”. This App enables surveyors in the field to provide direct and real-time feedback to the project management on the progress of data entry.
The dictionary describes the term „to plop“ as a „slight popping noise“. As soon as a point is processed in the field, this information appears, i.e. „plops“ onto the screen of the project manager.
PLOP is an EFTAS in-house design and was developed to support and coordinate a large number of surveyors in the field with a simple tool in the event of low mobile network coverage. PLOP allows dealing with short term capacity shifts if the progress of data entry is slowing down or speeding up for whatever reasons.
The App has proven itself in large scale mapping projects such as LUCAS or field surveys in Africa.
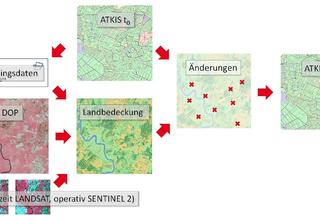
05.12.2015Sought and found.
The automated update of the ATKIS©-Basis-DLM through remote sensing. read more05.12.2015Sought and found.
The automated update of the ATKIS©-Basis-DLM through remote sensing.
Please have a look at the following images:
Can you detect any differences? There are 10 dissimilarities to be found?
In principle, you have just conducted an on-screen change detection. You have manually compared two similar data sets searching for differences. A similar manual process is currently the standard for the update of geographic base data at the “Landesvermessungsbehörden” (land survey offices) throughout Germany.
EFTAS and the State Agency for Surveying and Geoinformation of Schleswig-Holstein (LVermGeo SH) have been looking for alternative solutions to update geographic data bases. „DLM-Update“ describes the concept to optimise and accelerate the detection of changes to the ATKIS©-Basis-DLM through partly automated satellite image analysis.
Geographic base data from the LVermGeoSH have been combined with satellite imagery, made available through the European program Copernicus . Data from the satellite system Sentinel-2 will be used, as it provides cost free, high resolution and multispectral optical imagery with a high temporal resolution.
Remote sensing methods based on this data help to detect changes in comparison to the current data set. Based on a set of rules, the supervised classification results of land cover are compared to the real land use classes within the ATKIS©-Basis-DLM in order to automatically find indications for area changes.
With “DLM-Update”, the whole methodology is realised as a software prototype. GeoIT enables the robust, cost-efficient and automated analysis of remote sensing data within the existing GIS structure of the surveying authorities. The simple and user-friendly programming interface allows staff from the surveying authority to operate the programme without detailed knowledge of remote sensing.
By the way, did you discover all 10 differences? And do you think you managed quickly?
If you can answer both questions with “yes”, you should apply for a job with one of the relevant authorities. If not, this might be one more reason to look at “DLM-Update” as a useful instrument.
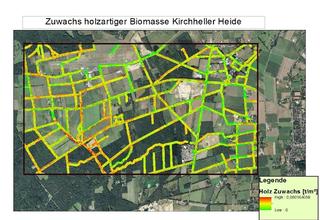
01.11.2015Biomass has great potential.
Landscape management materials for the generation of heat and electricity. read more01.11.2015Biomass has great potential.
Landscape management materials for the generation of heat and electricity.
Landscape preservation measures are expensive. BiomassMon offers a more economic solution. How? By implementing remote sensing data free of charge.
Traditionally, landscape preservation measures are carried out to comply with traffic safety duties and conservation guidelines. For public authorities and land owners it is first and foremost a cost factor. With the increasing importance and use of renewable energies, biomass has become a valuable product. The increase in the cultivation of corn underlines this development.
Materials produced from nature conservation and landscape management measures provide biomass that can be used to generate energy. No matter whether it is legally classified as waste or raw material. Instead of wasting green cuttings, using them for energy production is a better and reasonable alternative. From a financial viewpoint, expenditures can at least be compensated and if the energy production is successful, profits can be generated.
However, the energy content of the material is limited. Furthermore, there are different ways of utilisation. Only a local and systematic use makes sense from an economic and sustainable perspective. In compliance with traffic safety and ecology and integrated into a management system based on growth forecasts of all parcels for the coming years. This requires detailed knowledge. What realistic quantities of biomass are available where? This information is of great importance not only to plant operators but also politicians.
Currently, there is no database or registry with information on type, growth and extent of biomass from nature conservation and landscape management. This is where BiomassMon starts.
Remote sensing is the method of choice when it comes to the acquisition of large scale and systematic geoinformation. With the Copernicus program [link], Europe is currently establishing an autonomous European satellite infrastructure which will provide free of charge satellite data with a variety of new spectral and temporal resolutions. This opens up new application possibilities that were not possible before due to the high cost of remote sensing data. This is also true for the detection of biomass potentials for energy production.
Together with the institute Fraunhofer UMSICHT and the University of Hannover, EFTAS has developed a process to use Copernicus data. In addition, digital terrain models were used for analysis. The DTM’s were generated from orthophotos and laser data in order to derive the horizontal distribution and height of relevant vegetation classes. The remote sensing data delivers key figures such as the amount of substrate (grass and wood) and energy content that can be fed into a GIS. A demonstrator has already been realised within a WebGIS. These key figures based on remote sensing data allow site recommendations for biomass conversion plants together with investment cost estimates and the calculation of potential for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
The perspective is obvious. With BiomassMon, forecasts can be made to plan and conduct harvest and conservation campaigns more systematically.

18.11.2015Energy landscape Münsterland.
EFTAS presents WebGIS for monitoring of hedges at the 2nd Innovation forum. read more18.11.2015Energy landscape Münsterland.
EFTAS presents WebGIS for monitoring of hedges at the 2nd Innovation forum.
Of course, the stronger use of renewable energy sources will have its impact on the landscape.
At the ‘Gut Havichhorst’ near Münster a vision for the Münsterland was presented. The meeting was initialized by the ‘Lebenswerte Landschaft‘ (precious landscape) foundation, and it was informative as well as exiting. Controversies were not avoided. As usual very lively was the discussion on the possibilities of extraction of natural gas in the Münsterland.
The strong opinions and emotions on both sides made it clear that objective information is needed. Current geo information can deliver an objective input. Innovative GeoIT concepts are welcome.
At the exhibitioners desk EFTAS presented his BiomassMon-WebGIS-Prototype. It demonstrates how on the basis of satellite imagery , the energy potential of wood from hedges, a typical element of the Münsterland, can be determined. With objective information at hand it is much easier to combine the goals for energy, ecology and landscape quality.
[18.11.2015] Energy landscape Münsterland.
EFTAS presents WebGIS for monitoring of hedges at the 2nd Innovation forum. … [read more]
15.10.2015Find your own route.
„Erlebnis Naturerbe“: a routing system based on App and web portal. read more15.10.2015Find your own route.
„Erlebnis Naturerbe“: a routing system based on App and web portal.
Nature tourists in the municipality of Coesfeld are not guided within fixed tours and themes. The “Erlebnis Naturerbe”, a routing system based on an App and web portal, allows the visitor or tourist to plan their own and individual routes to explore the nature and the landscape of one of the largest districts of Westphalia. Whether by foot or by bike, visitors and tourists can explore conservation areas and nature reserves as well as other cultural highlights. Places of interest are equipped with information boards providing interesting and detailed background data on local flora and fauna as well as the European dimension of these protected areas. Within the system „Erlebnis Naturerbe“, conservation-related topics are processed and integrated into the routing and information portal.
By choosing “points of interest” (POI), the user can select specific topics and add them to his or her own individual route planning.
The development of the App as well as the technical implementation of the web portal was realized by EFTAS.
The data basis for the system includes specialised geodata from the North-Rhine Westphalia State Agency for Nature, Environment and Consumer Protection (LANUV NRW) as well as regional and local data from the nature conservation centre of the municipality of Coesfeld e.V. The data basis for the routing includes official geodata from the bicycle route planner of North-Rhine Westphalia as well as local information on walking trails.
Data management was realised by expanding the semantic model and exchange format „XErleben“, a data base containing information on leisure activities. As a result, the compatibility with state touristic data is guaranteed. “XErleben” is based on a data model developed by the Land Survey Office, containing a registry of leisure activities. The model consists of a GML application diagram and a catalogue of signatures. The diagram allows the provision of data via OGC-compliant web mapping and web feature services. The categorisation of POI’s follows a hierarchical thesaurus. The data storage of POI’s and the routing network follows a database solution based on PostgreSQL/PostGIS. The provision of data for visualisation and route calculation is managed via a REST interface (HTTP-based web-service interface).
To visualise nature themes within the App and web portal, the user is offered a visual network of themes which can be changed and explored intuitively via touchscreen. The network’s nodes provide thematic profiles. Desired themes can be used as parameters in future route calculations. The structure of the network (nodes, neighbours, describing text) is defined by a configurable XML file.
To enable data maintenance and update of the POI’s and routing data, an online geo-editor was established. This editor provides the nature conservation centre Coesfeld as system operator with a user-friendly possibility to update POI’s and routes via web browser. By temporarily closing individual sections of the route, visitor or tourist movements can be influenced, f. ex. to avoid disturbance to nesting birds.
The web portal is based on the open source publishing system WordPress. A JavaScript framework and OpenLayers were used for the map application and the geo-editor backend. A hybrid approach through a combination of HTML5, JavaScript und CSS3 was used for the development of the App. In combination with the open source Cordova Framework, this approach allows the development of mobile applications for different operating systems such as Android (Google), iOS (Apple) and Windows Phone (Microsoft) on the basis of a joint programming.
For a practical example, please go to: http://www.erlebnis-naturerbe.de/.

13.11.2015Copernicus-Forum 2015.
We were there. read more13.11.2015Copernicus-Forum 2015.
We were there.
The title of the forum „Copernicus Erfolgreich Nutzen“ emphasizes the use of Copernicus data and services for science, economy and management. Further potential applications of the data were presented. This is what can be taken from the website d-copernicus.de. The forum is in fact getting more relevant every year.
The DLR has invited interested parties in cooperation with BMVI, BMI, BMUB and BMEL. The value of remote sensing and geo informatics for management purposes is recognized more and more.
Of course the Copernicus program takes advantage of the fact that the first operative Sentinel satellites make the possibilities for application more concrete. That’s also what the many visitors in Berlin noticed.
That is also what made our presence rewarding . We presented some of our Copernicus projects - BiomassMon, DLM-Update, Natura2000 Monitoring and GMES4mining- and became some constructive comment.
Quelle Bild und Homepage „Copernicus in Deutschland“: http://www.d-copernicus.de/
[13.11.2015] Copernicus-Forum 2015.
We were there. … [read more]
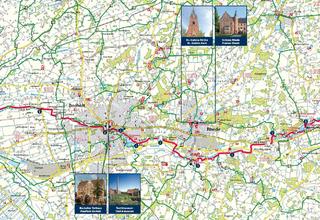
15.10.201551 km of river Aa.
An App for bike tourism around the area of Isselburg, Bocholt, Rhede, Borken and Velen. read more15.10.201551 km of river Aa.
An App for bike tourism around the area of Isselburg, Bocholt, Rhede, Borken and Velen.
The Bocholt Aa is a small river in the western part of the Münsterland region. Being the result of three rivers meeting in Velen, the river Aa takes another 51 km before meeting the Dutch river Issel in the city of Ulft. The bike route of the same name follows the Bocholt Aa the whole way. This bike route, which is particularly scenic and touristically well developed, runs through the middle of the „Münsterländische Parklandschaft“ (Münsterland park landscape) and nature park “Hohe Mark”. Wide open fields alternate with small forestry areas and river meadows. Along the way, Cafés and little quaint villages invite the tourist to stay.
The App „Bocholter Aa“ which was developed by EFTAS, now involves the entire region surrounding the Bocholter Aa into bike tourism.
With the help of this App, tourists and day visitors can easily plan their own individual route through the region Bocholter Aa. The App turns the Smartphone into a navigation tool and travel guide at the same time. The above bike route is obviously the core element of the App, but alternative routes such as a combination with thematic routes like the 100 castle route or flamingo route are also possible while the App provides valuable and practical information on regions and cities all the time. What else is important for the tour rider?Restaurants, accommodation, public transport, camp sites, bike rental or e-Bike charging stations?
You will find everything in the App “Bocholter Aa”! Please find out for yourself!
01.10.2015Piling up.
Anthropogenic deposits and the extraction of recyclable materials contained therein. read more01.10.2015Piling up.
Anthropogenic deposits and the extraction of recyclable materials contained therein.
Blast furnace slag, converter dust and toxic gas sludge. Old waste dumps still hold a lot of useful recyclable material. Process-related it is mainly iron. For a while, phosphate-rich sludge was also stored in waste dumps. With increasing prices for raw materials it is becoming economically interesting to develop these resources in the near future.
With regard to economic feasibility studies, the resource volumes in smelter heaps must also be known. What methods are best suited to recover these resources? The question arising is: Where are these waste dumps? The aim of the project „REStrateGIS“ was to establish a national resource land register for smelter heaps. This cadastre gives an overview on the location of waste dumps, stockpiles and other landfills. Ideally, it also provides information on the content.
Through automatic analysis of satellite data, EFTAS could detect possible locations of heaps. Elevation data was derived and analysed, texture and structure analyses were conducted, spectral indices of potential recyclable materials were identified and data on vegetation succession was used as an indicator for acid or iron-rich soils.
The results were combined with research data from the Fraunhofer institute UMSICHT.
As part of the project „REStrateGIS“, national archives and land registries on contaminated sites were checked and archives of mining authorities and companies analysed. In future, it will be possible with a click to bring up the desired deposit in large format. Additional data on historic and current aerial photographs, photos with information on heap bodies and their substances will also be available.
One of the heaps served as a model case and was examined in more detail. Following expert interviews, screening of historic documents and inspection of the area, the samples underwent chemical analysis. As a result, the substances could be accurately listed. With the help of a reflection spectrometer, the spectral fingerprint of different materials could be measured and stored in a database. This database enables a targeted search in unknown heaps to gain first information on the materials that can be found at this location.
„REStrateGIS“ was developed in close cooperation with Fraunhofer UMSICHT, the Faculty of Geosciences and Geography of the University of Halle, the FEhS (Institut für Baustoff-Forschung e.V.) and EFTAS. Jochen Nühlen, one of the scientist of Fraunhofer Umsicht who was significantly involved in the project, assesses the perspective of “REStrateGIS“ as follows: „In future, it might even be possible to use the method to conduct detections of heaps worldwide – also in areas where the archives contain little data”.

01.10.2015No sign of data reduction.
Data-Mining with geodata for non-police hazard defence and energy industry. read more01.10.2015No sign of data reduction.
Data-Mining with geodata for non-police hazard defence and energy industry.
The Office of Technology Assessment at the German Parliament (TAB) views the innovative technology of data mining as a socio-political and legal challenge. As a consequence, expert reports were commissioned. EFTAS contributed with a case study on data mining with geodata.
Data mining does not deal with the generation of new data, but with the extraction of relevant knowledge from large databases (big data), also called “Knowledge Discovery in Databases“. The goal is to find regularities, laws and hidden connections.
The search for patterns that display new and nontrivial information – the essential feature of data mining – has always been a central element of GeoIT and remote sensing. Therefore, data mining with geodata has a certain tradition.
This longstanding development was compiled into a study by an expert team at EFTAS. The study examines many individual subjects in connection with data mining with geodata. Definitions, data sources, processes, infrastructures, legal and ethical requirements and business models. These individual topics are illustrated with examples such as the emergency mapping in the context of non-police hazard defence and grid management in the energy industry.
EFTAS could demonstrate with this study that there is a potential for future-oriented application options with data mining on the basis of geodata and that the number of operational applications will rise in the future.
In future, more and more data with spatial reference will be available. However, we will also have to deal with unsafe data sources, data gaps or qualitatively inferior data. Data mining will be capable to extract valuable knowledge from this data and therefore become a key technology in the future.
01.10.2015Sustainable tourism.
Web portal & App for the nature tourism in the Rheinaue region. read more01.10.2015Sustainable tourism.
Web portal & App for the nature tourism in the Rheinaue region.
Low-impact tourism, sustainable and contemporary. A nice concept that is applicable wherever the landscape is ecologically as well as touristically valuable. A prerequisite to achieve this concept is a certain control of visitor movement which accommodates nature conservation, recreation and environmental education.
This was the intention of the pilot project “Rheinaue erleben” which was sponsored and promoted by the EU and the state of North-Rhine Westphalia. The municipality of Kleve has several conservation areas of European significance („Natura 2000“ ) with endangered animal and plant species as well as unique habitats.
With the help of modern GIS, GPS and communication technologies, these landscapes can be developed for tourism in a sustainable way. To achieve this goal, individual and theme-oriented tours are offered for hikers and cyclists.
In close cooperation with the nature conservation centre of the municipality of Kleve, EFTAS realised a concept based on a web information portal and routing App. The web information portal is meant to be used for the planning of holidays “from home”, the information and routing App “on site”.
The internet portal www.rheinaue-erleben.de and the associated App help to plan hiking or bicycle routes along the Rheinaue between Emmerich, Rees and Kalkar and offer information on natural and cultural aspects at the same time. Interactive maps provide detailed information on nature, cultural characteristics and gastronomy. Interesting points along the way are featured with text, photos and fascinating stories, so-called listening experiences.
Visitors not only learn about conservation areas and their endangered animal and plant species but also about the Rhine, castles and palaces along the way.
The individual route can already be planned at home on the computer. Based on the themes and additional requirements such as time and distance, the portal calculates a route which is perfectly tailored to the visitor’s needs. New is the possibility to calculate A to B routes as well as round trips.
The route is then followed via App. All routes can be transferred to the smart phone and then retrieved en route. The application displays local information on nature conservation themes supported by multimedia such as film, video, text and photos. However, spontaneous route calculations are also possible. The navigation function keeps the visitor on track and offers information on the next point of interest.
Expert opinion:
"The map portal with associated App has helped us to successfully market our natural values between Emmerich, Rees und Kalkar to our visitors in a modern way. At the same time we can now guide our visitors on predetermined routes to the highlights of the region in an environmentally sustainable way".
Melanie Brinkmann, Project Manager Nature Conservation Centre Kleve.

01.10.2015Hiking in former mining areas.
Theme routes and mountain trails in the northern Ruhr area. read more01.10.2015Hiking in former mining areas.
Theme routes and mountain trails in the northern Ruhr area.
Several mining dumps in Vest Recklinghausen bear witness of the significant past of mining in this area. The municipality of Recklinghausen came up with the idea to realise the value of these reminders of mining activity in the northern Ruhr area for tourists by developing a smartphone App for iOS and Android.
As a consequence, EFTAS developed the so-called “Halden-Hügel-Navi“, an App that guides smartphone users via 12 theme routes and 150 “story-telling-stations” through the mining areas of the Vest.
The App delivers information on times of pre-industrialisation with castle complexes and swamp forests to the peak phase with rapid industrialisation and development of waste heaps as well as the massive structural change with phases of renaturation and conversion. The tourist experiences the present situation by taking the tour.
Because classical signage with information boards and signs is prone to bad weather or destruction, the municipality of Recklinghausen decided to implement a purely mobile routing system which is offered to tourists in the form of a smartphone App free of charge. Tourists are guided via visual and acoustic navigation – it also works if there is no mobile reception!
It is important to mention that you cannot use the App on your sofa at home to digitally explore the highlights of the region as most of the interesting information only becomes available when reaching the corresponding point of interest in the field. In the App, hikers can tick off the mining heaps reached on their tour and then participate in raffles with their virtual stamp booklet.
The App is further supplemented with the integration of additional points of interest such as gastronomy, accommodation, the possibility to download maps and information on public transport including stops and timetable information.
Expert opinion:
„The terms of reference for the App were challenging: the App was meant to provide mobile access to the content of all theme routes as well as touristic information. At the same time it was requested that the App provides clear navigation along the theme routes without signposting in the landscape as well as the possibility to be used offline. Both requests have been achieved – the App is technically well thought through and easy to use. “
Sven Ahrens, Project Manager Municipality of Recklinghausen.
30.09.2015Good luck!
Hyperspectral and earth movement monitoring of mining areas. read more30.09.2015Good luck!
Hyperspectral and earth movement monitoring of mining areas.
Prospection, exploration, production and recultivation of abandoned mining areas are the main phases of mining operations. These phases all need geoinformation. Remote sensing methods are becoming increasingly part of the relevant processes.
As a result of the project GMES4Mining, EFTAS has developed two methods as services to Copernicus, the European Programme for the establishment of a European capacity for Earth Observation: the search for deposits by defining mineral reserves and the detection of earth movements through continuous earth observation. The search for metal ores, rare earths as well as raw materials of all kinds is of great significance. Each material reflects the sunlight in a quite specific way.
Humans perceive this as different colours. Even within the non-visible radiation ranges, different reflections occur. This is used by bees for orientation purposes within the UV spectrum and by snakes to detect thermal infrared radiation. So called hyperspectral sensors are able to break down reflection values into more than 100 individual units of information.
Under laboratory conditions, materials can be described by their characteristic spectral signature which is then used to find these materials in the field with the help of hyperspectral remote sensing. The GMES4Mining practical test in Australia produced some very promising results with regard to the detection of different ores and minerals.
From exploration to production.The extraction of mineral resources usually involves the movement of large volumes of upper earth crust material. Not all of these earth movements are wanted. Subsidence, landslides and open pit mines cause problems during production as well as rehabilitation of former mining areas.
The methodology developed by EFTAS within the GMES4Mining project is based on the analysis of airborne and satellite imagery and allows the detection of first signs of subsidence and lowering of the groundwater table. Indicators are values like soil moisture and signs of water logging within vegetated areas.
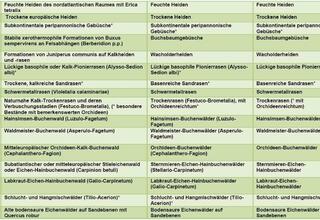
01.09.2015Every 6 years!
Remote sensing based field data for an efficient FFH monitoring. read more01.09.2015Every 6 years!
Remote sensing based field data for an efficient FFH monitoring.
The military training area Senne in East-Westphalia is a quiet piece of earth, unless there is a military maneuver. Nature has been able to develop here almost undisturbed which is why this training area has protection status. It fulfils the criteria of the European Flora-Fauna-Habitat Directive (FFH-RL in Germany).
FFH areas accommodate animal and plant species and habitats that are threatened European-wide. In total, the FFH Directive
lists 231 habitat types and more than 1.000 animal and plant species. The Directive defines that the conservation status of FFH areas has to be regularly checked and monitored. This has to happen every 6 years. Traditionally, these habitat areas were mapped by surveyors in the field. However, this is expensive and time-consuming. In the case of the military training area of Senne, habitat types on an area close to the size of 17.000 soccer fields have to be monitored in one run.
EFTAS has developed a more efficient approach.
For this purpose, remote sensing methods are implemented in preparation of the field surveys. Geometries of habitat types are exactly delineated on the basis of satellite and aerial images. This happens to a large extent automatically. Additional data from forestry maps and biotope mappings are also included in the analysis.
The geometry information generated is used by the surveyor in the field, who then has considerably less work to do. The experience from NLU, who is responsible for the field surveys and a long term cooperation partner of EFTAS, shows that 9 out of 10 habitat or biotope types can be correctly delineated geometrically with remote sensing methods. This allows the surveyor to concentrate on what he can do best: identify and collect conservation relevant data for the typification of biotopes and habitats.
The client benefits from better results and faster processing times. In case of the military training area Senne it is the Federal Authority for Real Property Administration (Bundesanstalt für Immobilienaufgaben).
01.09.2015Know your local area.
Visitor information system and management tool „Tourenplaner Münsterland“. read more01.09.2015Know your local area.
Visitor information system and management tool „Tourenplaner Münsterland“.
The Münsterland region is a popular holiday and recreation area located between the Netherlands, the Teutoburg Forest and the Ruhr district. Cyclists and equestrians in particular find a large choice of routes through an interesting and varied park landscape.
According to specifications of the customer, a web portal incl. App was developed to inform guests in advance as well as serve as a consulting and management tool for the local tourist information Münsterland e.V.
EFTAS has realised this idea with the “Tourenplaner Münsterland“.
The tourist is addressed through an integrated visitor information system with map portal and individual thematic routes. They can plan their own bicycle or equestrian routes upfront and receive recommendations for round routes that are perfectly matching their own personal wishes – the corresponding App helps the user to navigate on site.
Cyclists and equestrians can choose from a variety of qualified routes such as the 100-Castle-Route or the Flamingo-Route. Moreover, they can plan their own individual routes matching their requirements. Whether family outing or sophisticated racing bike route – the routing engine calculates a varied A-to-B route or round trip depending on desired duration or driving profile. Previously chosen priority themes and interests are also taken into account.
To be successful, a visitor information system constantly needs up-to-date and high quality data – from opening hours or entrance fees to perfectly accessible bike paths. The management tool “Tourenplaner Münsterland“ concentrates all relevant information in one central place. The management of all this data is done with XErleben, an object-based model for INSPIRE-compliant standardised data exchange in administration, tourism and economy.
Timeliness of the data is ensured through online editor functions and image analysis techniques: touristic scouts can make modifications directly to the web portal. These are immediately published online or released after having been checked by a quality controller, depending on the rights of the user. New routes can be added, existing routes can be changed and information on places of interest can be edited.
Expert opinion:
„The Tourenplaner Münsterland is our central platform for all relevant information concerning the Münsterland region. Information is continuously updated via online editor and image analysis techniques. On the basis of this latest information, tourists are able to plan their tailor-made bike tours and horse rides to the highlights of our beautiful holiday region“.
Hans-Joachim Gerdemann, Project Consultant Münsterland e.V.
15.08.2015AgroSurvey.
ArcGIS extension for the control of agricultural subsidies. read more15.08.2015AgroSurvey.
ArcGIS extension for the control of agricultural subsidies.
For the farmer the agricultural parcel is a uniformly cultivated piece of land. European farmers can apply for EU agricultural subsidies for their agricultural parcels. However, a significant number of aid applications are controlled. In Germany, EFTAS is the leading service provider for these controls. The applications are evaluated directly on the screen, assisted by a GIS (Geographical Information System) and on the basis of airborne and satellite imagery. A great amount of geoinformation is needed in order to conduct these controls precisely.
EFTAS employees, who evaluate the applications for agricultural subsidies, have to incorporate data from different sources: airborne and satellite imagery, application data, cadastral information, valuation codes and much more. To achieve this, EFTAS uses an in-house developed GIS extension for ArcGIS Desktop by ESRI.
This EFTAS solution is called AgroSurvey.
This GIS extension allows users to organise and link existing applications, cadastral data and the geometry of training fields as well as attribute data in geographic databases. It also structures the operational process and enables an efficient processing via intelligent entry masks.
The agricultural parcels of land to be evaluated are selected from the data window. By selecting the Personal Ident (PI) of the farmer and the Parcel ID, the visible map section is centred on the area including the agricultural parcel to be evaluated. Information on size, land use and number of involved fields as the key identification data of the cadastral unit are also provided.
Following the interpretation of the imagery and the comparison of evaluated data with the application data, the geometry of the agricultural parcel is adjusted if needed according to the limits of utilisation.
To support the interpretation of land use, training areas with known land use including photos can be accessed.
Finally, the interpretation results are specifically coded and integrated into a database for further analysis.

01.08.2015Something for careerists.
Travel guide App „Platzhirsch“ for a modern tourism marketing including crowdsourcing. read more01.08.2015Something for careerists.
Travel guide App „Platzhirsch“ for a modern tourism marketing including crowdsourcing.
Each of us knows such a case: if we are not familiar with a place, we tend to use our smart phone to find the right way. And we are also familiar with the following case: before making any purchase decision, we study internet ratings, tips and recommendations. What could be more reasonable than picking up these two trends to combine them into an App for travellers? Especially in tourism, insider knowledge and experiences of other travellers play a huge role when choosing holiday destination, places of interest or a restaurant.
What we obviously need are: geodata and content.
With “Platzhirsch”, administrative geospatial or specialist data are integrated into the App’s universal data structure through standardised interfaces. Subsequently, the application for iOS, Android & Co. is created almost with a simple push of a button. Advantage: the information update is conducted by the relevant agencies and the data is automatically and centrally visualised in the new application. Positive side effect: this simple „push of a button“ makes the processing cost-effective. As a consequence, the system is affordable for small and medium-sized destinations.
„Platzhirsch“ also allows the user to add popular insider tips and comments. Via crowdsourcing. Registered users can rate the existing content or add further tourist services and products. Therefore, “Platzhirsch“ is both a rating and marketing platform.
„Platzhirsch“ was developed in close cooperation with the technical college Münster and the district of Warendorf, which, in its role as a pilot user, participated in the definition of data structure and operating concept.
„Platzhirsch“ is a cost-effective ready-to-use product for an individual mobile travel guide for municipalities, cities and regions of every size. A win-win situation for both well informed travellers and those responsible for the effective marketing of destinations.

15.07.2015Malawi is eager to know.
Yield forecast with field survey and remote sensing. read more15.07.2015Malawi is eager to know.
Yield forecast with field survey and remote sensing.
Corn, tobacco, cotton, rice, soy, sweet potato, manioc, peanuts and tea. It is common knowledge that these are the main crops grown in Malawi. However, the aim for the future is to have more reliable data on where in the country the crops are grown and what the expected yield will be.
Meanwhile, the Ministry of Agriculture initiated a country-wide survey of agricultural parcels, which was conducted by EFTAS under the lead of Consorzio ITA.
To achieve this, an innovative combination of field survey and remote sensing was chosen. Within a couple of weeks in 2014 and 2015, 25.000 sample points were surveyed by means of air photo interpretation and field survey. This data was used to calculate informative statistical analyses.
Malawi has shown that yield forecasts can be achieved on an operational level through a combination of field survey and remote sensing. In 2015, Consorzio ITA and EFTAS conducted the random sample stratification, the field survey including preparation, training and management as well as the data analysis.
However, it would be desirable, if further campaigns could be increasingly conducted by the local authorities themselves.
15.07.2015Seeds instead of steppe?
Land management for the Western Siberian Grain Belt under a changing climate. read more15.07.2015Seeds instead of steppe?
Land management for the Western Siberian Grain Belt under a changing climate.
We are in Western Siberia. North of Tyumen. Grain fields as far as the eye can see. This is not a snapshot, this is a future scenario. Scientists are currently investigating whether the “Western Siberian Grain Belt“ will expand to the north due to climate change. Momentarily, uncultivated swamps and forests can be found in the transition zone between forest steppe and Pre-Taiga.
This transition zone between forest steppe and the northern boreal forest in Western Siberia is of global significance in terms of food production, carbon sequestration and biodiversity. Therefore, the previously mentioned scenario is probably not the ideal future. It is desirable to preserve biodiversity and productivity of agricultural ecosystems as well as semi-natural areas, which are scattered among the agricultural landscape. The question arises whether it would be possible to increase productivity on these already cultivated areas through sustainable intensification without causing negative environmental impacts?
The aim of the interdisciplinary joint project SASCHA is to analyse and evaluate different forms and intensities of land use on ecosystem goods and services in the Tyumen province. The purpose is to develop sustainable adaptation strategies to climate change and appropriate management tools.
It all starts with observation. With “SASCHA MS”, the SASCHA monitoring system, EFTAS has developed a software prototype to constantly update land cover data. One of the key functions of this monitoring system is the quantification of agricultural changes. The system development takes into account local requirements and conditions. It is able to support local decision makers in terms of large scale environmental monitoring.
SASCHA is part of the BMBF-funded measure “Sustainable Land Management“ Module A "Interaction between Land Management, Climate Change and Ecosystem Services". All activities with regard to research, development and implementation are conducted in close cooperation with Russian partners from science, industry and administration.

10.06.2015Taking new paths.
Geoinformation for traffic infrastructure planning. read more10.06.2015Taking new paths.
Geoinformation for traffic infrastructure planning.
Distances, heights and spatial volume. These are important parameters on every large traffic route construction site. These angle and distance measurements are recorded by surveyors with their theodolites. Right from the design phase, precise 3D terrain data is needed for these construction projects. To evaluate alternative routes, to plan construction works and to prepare process logistics.
EFTAS prepares planning documents for the design process of traffic route projects.
In case of large-scale projects, the application of remote sensing and GeoIT is an economically sensible approach. This is also known to the relevant authorities in North-Rhine Westphalia. The state is large and has a high motorway density. Therefore, remote sensing based geoinformation is often used in building projects. EFTAS has already provided this type of information for a variety of projects. It is a well-established process to take aerial photographs, convert them into stereo orthophotos which can then be used to derive 3D geoinformation through photogrammetric methods.
The most important processing steps are the planning of the aerial survey, the signalization and the determination of control points as well as the orientation through aerial triangulation. In the course of data collection, all relevant object types receive information on height and position. Objects, that cannot be clearly identified, are checked in the field. The stereo orthophotos are also used to produce a digital terrain model (DTM). The original data is delivered digitally and in all GIS and data formats.
EFTAS produces planning documents for an immediate use of the data: orthophoto maps derived from a superimposition of aerial photographs, ancillary and client data as well as classic line plans. Both data can be delivered in printed format or as a pdf-document.
As an add-on, EFTAS also collects information on noise-relevant objects and processes this data for the use in noise calculation programs. Due to legal requirements, the construction of new roads and the reconstruction of existing roads have to comply to limit values of traffic noise. Therefore, information on neighbouring houses like eaves and ridge height, roof windows, balconies, verandas and other objects like traffic lights, car parks and bridges is also of high relevance.

01.06.2015Level-up.
A global agricultural monitoring network for the sustainable increase of food production. read more01.06.2015Level-up.
A global agricultural monitoring network for the sustainable increase of food production.
Worldwide, agriculture plays a huge role. It is the basis for food production for a steadily increasing world population and also responsible for cultivation and conservation of our cultural landscapes. In coming years, the food production needs to reach a more productive level especially in developing and emerging countries without affecting cultural assets and natural areas.
Besides traditional crops, new methods of cultivation as well as new crops can help achieve this goal. However, introducing new crops and new methods is not without risks. Due to their historical development, traditional crops have adapted well to the natural environment. Therefore, the introduction of innovative cultivation methods needs to be closely monitored. What is their influence on the ecosystem, what is their influence on productivity?
Remote sensing methods for global agricultural monitoring are already available. There are various individual projects. The aim of SIGMA (Stimulating Innovation for Global Monitoring of Agriculture) was to create an international network of experts to consolidate different monitoring methods (evaluation of methods, comparison of results etc.).
Capacities from Europe, Asia, Africa, South America and the United Nations are involved in the project. SIGMA is part of Europe’s contribution to the GEOGLAM (Global Agricultural Geo-Monitoring) initiative, which is a key component of GEO (Group on Earth Observation).
This initiative was launched by the G20 group of states and aims to strengthen the worldwide collection and coordination of spatially relevant data.
EFTAS has contributed with its expertise by developing a standardised process called „data collection & validation protocol“.
This process describes the professional collection of field data to ensure a reliable accuracy assessment of remote sensing data. It also delivers guidelines for standardised field data formats incl. instruments, manuals and training materials.
In order to determine the influence of new crops or new farming techniques on the ecosystem and productivity, agricultural areas and crops as well as their impact on the environment are analysed with satellite imagery.

01.06.2015Trust is good but control is better!
Sampling inspection of European agricultural direct payments by means of remote sensing. read more01.06.2015Trust is good but control is better!
Sampling inspection of European agricultural direct payments by means of remote sensing.
There is help available for European farmers. The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) allows planning security through income and risk protection. Direct payments that are independent from production represent the core element of the EU agricultural support.
They soften fluctuations of agricultural prices and also recompense the services provided by farmers to society by maintaining cultural landscapes and natural resources. Approximately 16 million km2 of Europe are eligible agricultural area. This is twice the size of Australia. Obviously, there are some farmers that claim more from the fund than they are entitled to. Therefore, controls are carried out.
In Germany this is done through the Integrated Administration and Control System (IACS) with the support of GeoIT.
Since 1994, EFTAS has been commissioned every year to check claims by means of remote sensing. On average this has been done for 6 non-city states. EFTAS also coordinates the recording and processing of required aerial and satellite imagery. The latter form the basis for the visual interpretation of those agricultural parcels for which aid is claimed.
This is done following a differentiated key within the GIS and partly through on-site checks. The results are passed back to the agricultural administrations for legal assessment.

01.06.2015Ortho. . .what?
Benin – geoinformation based on airborne and satellite imagery. read more01.06.2015Ortho. . .what?
Benin – geoinformation based on airborne and satellite imagery.
Benin is a disadvantaged country. Just like other African countries, Benin is confronted with the traditional challenges dominating its development: supply of water and food security for a growing population.
However, the farming sector has development potential. Large areas of the country have the potential for cultivation, but only one-sixth of the total land area has been utilized so far. An environmentally sustainable land management should be pursued in order to prevent a further worsening of already existing environmental problems such as increasing deforestation.
EFTAS has created an up-to-date map series at a scale of 1:5000 as a basis for sustainable land management. The basic geoinformation for this map series was derived from the analysis of satellite imagery.
Airborne and satellite imagery have to be available in a distortion-free and true to scale orthophoto format in order to be usable for surveying and planning projects. To achieve this, satellite imagery is projected onto a georeferenced 3D-terrain model.
In Benin, EFTAS produced such a 3D terrain model from older aerial photographs.
In order to create such a 3D terrain model every point on the earth’s surface has to be recorded from at least two different perspectives. This enables the calculation of 3D models. Within the discipline of photogrammetry this is also named stereographic processing. In principle, the human eye follows the same concept.
For the production of these satellite imagery based maps, a variety of satellite systems like Quickbird, GeoEye or WorldView 2 were used. Objects of 50 cm in size can be differentiated on the Earth’s surface. Therefore, single landmarks like intersections, corners or other obvious structures are visible.
To generate these landmarks, point coordinates were collected on the ground using precise GPS measurements. These point coordinates were then used to project the satellite imagery onto the corresponding points in the 3D model. As a result, satellite images in orthogonal projection were created.
In the case of Benin, EFTAS generated maps for 10 rural communities at a scale of 1:5000 based on 14,000 km² of orthophotos.

01.05.2015Sustainable development.
Development cooperation for food security in Africa. read more01.05.2015Sustainable development.
Development cooperation for food security in Africa.
The subject of food security remains a continuous challenge in Africa. In order to timely assess yield and food security, basic information is often missing: how large is the area under cultivation? Which arable crops are cultivated where? How is the stage of development of these crops?
GeoIT-based monitoring services can provide important answers to these questions. These services allow systematic crop monitoring services in order to develop early warning systems. The European Space Agency (ESA) established the so called Global Monitoring for Food Security (GMFS) program which aims to provide earth observation and GIS based services within the framework of food security. Several African states were selected for pilot projects.
Sudan is a good example for the successful transfer of technology. For EFTAS, the aim of the development cooperation with the Sudanese Ministry of Agriculture and Irrigation was to implement Geo-IT methods through external experts and as well as enable local authorities to independently apply Geo-IT methods for food security on a continuous and operational basis.
To realise this technology transfer, a wide range of applications was put together: the combined use of medium and high resolution remote sensing data, the integration of optical and radar data and the integration of agricultural field spot checks.
For all processes, EFTAS conducted professional in-house and field trainings with customised training material.
EFTAS also accompanied the cooperation with great commitment until Earth Observation and GIS based services in Sudan were working on an operational level. A genuine success for all parties involved and a good example for the rest of Africa.
As other African countries would like to follow the example of Sudan, ESA and other development cooperation organisations are investigating possibilities to expand this form of effective and practically-oriented technology transfer.

01.02.2015Where, when and how much?
GeoIT in the energy sector. read more01.02.2015Where, when and how much?
GeoIT in the energy sector.
Smart grids play an important role for the decentralized power supply of the future. They act as the essential link between production, usage and storage. To ensure grid stability and intelligent power management, geoinformation is needed. How much energy is produced or stored where and when? Knowing just when, where and how much energy is flowing through the power lines means that the energy flow can be optimised. The energy sector is undergoing radical change due to the energy transition („Energiewende“).
There are new processes, new players and new demands. But how much GeoIT is needed where and when? The answer lies in a continuous cross-industry exchange.
EFTAS strongly engages in this dialogue and promotes the establishment of a network between technology and business. The development projects geonetNRW and geonet 2.0 evaluated these interfaces between energy sector and GeoIT.
Core processes, trends and application potentials were analysed and discussed among experts of both fields. The results of these geonet projects are documented in studies and can be accessed barrier-free.
01.01.2015Breakage and throw after the storm.
Detection of storm-damaged timber with CIR aerial photographs. read more01.01.2015Breakage and throw after the storm.
Detection of storm-damaged timber with CIR aerial photographs.
Strong wind incidents are becoming more frequent. Widespread windfall and wind throws in forests have become more common. Storm-damaged timber needs to be taken out of forests as quick as possible. The longer it takes to remove the deadwood, the higher the colonisation by insects and fungi will be. This minimises the economic yield expectations and maximises the probability for forest pests.
EFTAS recorded the areas of damage caused to forests with remote sensing techniques and established a basis for timber haulage logistics.
An example: During the night of 18th to 19th of January 2007, the storm “Kyrill” struck Germany. It caused considerable damage also in the forests of North-Rhine Westphalia. According to the ad-hoc assessment by the responsible State Forestry and Timber Agency (Landesbetrieb Wald und Holz NRW), more than half of the forest areas were affected. This area was too large for a short-term terrestrial survey of the detailed damage situation.
Therefore, EFTAS was commissioned to assess the exact dimension of damage on 38 % of the total area of North-Rhine Westphalia. This was done for the regions of Niederrhein, Eifel and Sauerland. The prevailing weather conditions with persisting cloud cover prevented the assessment of these damages with satellite remote sensing. As a consequence, CIR aerial photographs (CIR = Colour infrared) were taken during short cloud free time windows. Via red colouration, CIR aerial photographs visualise reflection values of vegetation in the Near Infrared.
These reflection values are very useful for the interpretation of vegetation. The aerial photographs were processed by EFTAS and combined with topographic maps and digital information on forest tracks into a Geographic Information System (GIS) in order to digitally detect storm damage.
For a fast entry, the areas with wind throw were highlighted as POI’s (Points of Interest) with ID-number, height above sea level, exposition and name and number of forestry office. In the end, the system contained 22.000 points. This data served as the basis for the establishment of the timber haulage logistics: the forest officials could prioritise the forthcoming forestry work and the truck drivers were automatically directed to the POI’s in ideal sequence.

01.12.2014Flyer: PFR Benin.
Realisation of orthophoto maps for land management. read more01.12.2014Flyer: PFR Benin.
Realisation of orthophoto maps for land management.

15.10.2013Flyer: GMFS - Global Monitoring for Food Security.
Space based Services for Africa's Agriculture. read more15.10.2013Flyer: GMFS - Global Monitoring for Food Security.
Space based Services for Africa's Agriculture.